Aluminum vs. Zinc Die Casting: Core Differences
Fundamental Process Characteristics
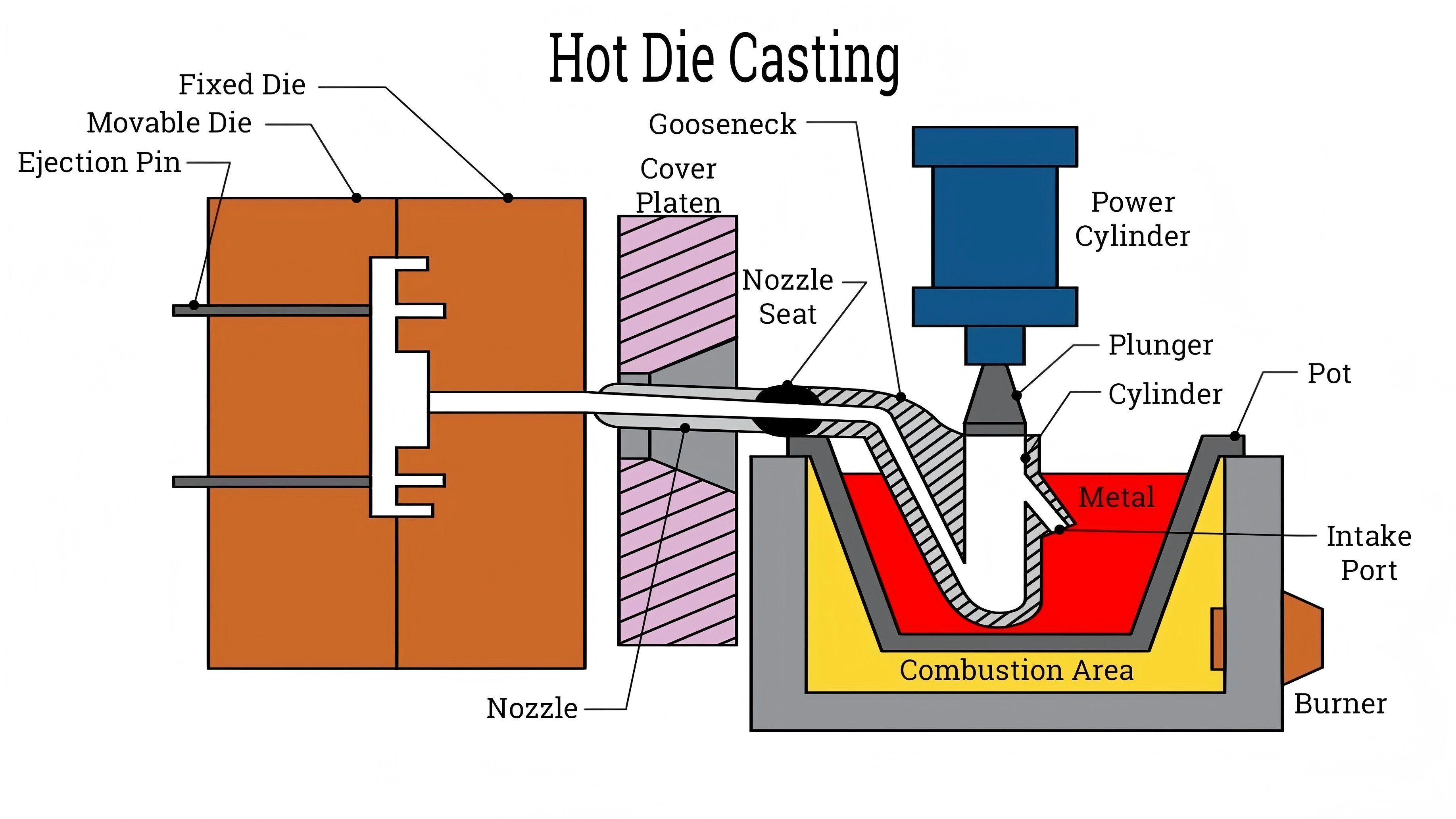
In general, when producing an aluminum die-casting, molten aluminum is ejected into a mold under high pressure. This process promotes a shorter cycle time and the ability to mold more complex parts since aluminum flows well at high temperatures. Zinc die casting is sometimes used for complex shapes or parts with thin walls and small openings, where high rigidity is required. Compared to other materials, zinc offers good formability and dimensional accuracy, especially in intricate mold designs. In some cases, nitrogen purging may be used during the casting process to help displace air and minimize oxidation in the mold cavity, improving overall casting quality. The ultimate aim of both aluminum and zinc die casting is to produce accurate casting quality parts, yet the mold type as well as setting times often differ. Knowing these differences can help companies choose the right material and process to meet their particular production needs.
Material Properties Comparison
Aluminum is also known for its strength and reliability, as it's not only a resistant material, but it enhances the life of related equipment, and since it’s lightweight, it is valuable in applications such as automotive and aerospace in which the reduction of weight is essential. While, on the other hand, zinc die cast parts are valued for their excellent shape stability and better surface finish for consumer goods, as consumer products demand attractive design. In the end, whether to use aluminum or zinc die casting parts comes down to the requirements of the specific application, such as weight tolerance, cost effectiveness and desired finish quality. Each of these materials provides a unique benefit that could have a great influence on the manufacturing process and product properties.
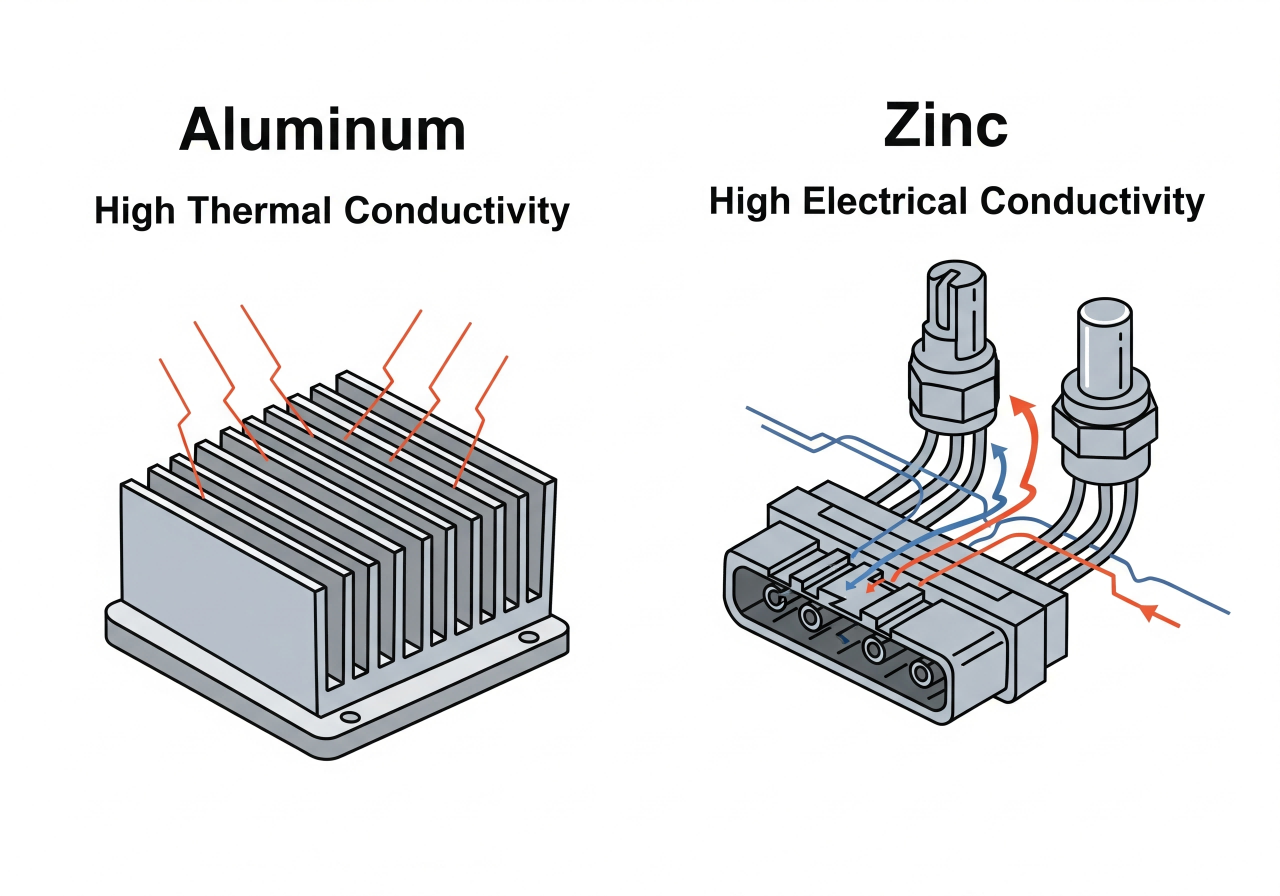
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Thermally, aluminum is good at conducting heat and is often used in applications where heat transfer is required, such as heat dissipation in electronics. Zinc does not have the same ability to conduct heat as aluminum, but it offers better electrical conductivity, making it suitable for electrical applications where it provides an efficient path for electricity to flow. And these conductive traits are critical information to determine if aluminum or zinc die casting should be used in these sensitive applications, such as electronics. Choosing the right material can improve performance and reliability in final product applications in which conductivity is important.
Aluminum's Strength-to-Weight Superiority
Aluminum is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and serves as an important material in industries including automotive and aerospace. This characteristic enables the vehicle to be light in weight and therefore very fuel efficient—a key requirement for modern-day transportation. Aluminum, furthermore, has a high resistance to stress and fatigue, which is a critical factor when producing high performance components with a long operational life. However, it is important to recognize that aluminum not only has great properties, but also that the production of aluminum profiles can be more expensive and also affect the cost of the project as a whole.
Zinc's Precision Casting Capabilities
Zinc die casting is known for its high precision, enabling thin walls and complex designs, which are desirable for consumer electronics. Zinc’s low melting point simplifies the casting process which shortens cycle times and saves energy, ensuring an economical production. However, zinc's mechanical properties, while advantageous for some uses, make it less applicable for products subject to mechanical stress than the more ductile aluminum. Because of that, zinc die casting is frequently chosen for applications where strength is lower than accuracy and detail.

Corrosion Resistance Comparison
When evaluating corrosion resistance, both aluminum and zinc alloys present distinct advantages depending on the application environment. Aluminum also offers good resistance to atmospheric conditions, with the need for protective coating being their main weakness in extreme conditions. Zn inherently has good corrosion resistance, which is often used as a protective coating for steel, such as in outdoor and industrial environments. The knowledge of these corrosion properties is important for the material selection for long lasting projects that will be performed in corrosive conditions.
Production Process Analysis
Zinc Die Casting Machine Requirements
There are specific requirements for machines to achieve the greatest production efficiency in zinc die casting. A good clamping force is needed to guarantee the precision of mould and to prevent a defect in the casting. Fast cycle times are also important in that they result in increased throughput and can greatly increase productivity. And you get what you pay for; quality machines can also lead to increased casting quality and consistency. Routine maintenance and retrofitting are essential to keep downtime down and production standards accurate. It is through the maintenance of machines, which may be overlooked, that we can avoid sudden machine breakdowns and reduce operation costs over time. Comprehensive knowledge of these ZN die casting machine requirements is crucial to the efficient production of quality castings.

Aluminum Die Casting Cycle Times
The aluminum die casting process generally has longer cycle times vs zinc die castings, especially in aluminum cooling cycle times. This is an important feature since it requires a careful consideration and control of cycle times by the manufacturer in order to achieve optimal production rates and minimization of costs in the production process. Aluminum’s higher melting temperature adds to these extended cycle times, yet advancements made to die casting technology offer a promising solution to resisting those extended cycle times. New cooling techniques and technology implementation are continuing to simplify aluminum die casting, contributing to more efficient, less expensive die casting overall. Being able to recognize what is considered a fast aluminum die casting cycle time is critical for you to obtain the balance and efficiency so that you can have the most production success.
Energy Consumption Patterns
A knowledge of the power demand of the zinc and aluminum die casting process is an essential requirement to introduce sustainable manufacturing. As a rule, aluminum die casting processes are also more energy-intensive as a result of higher melting temperatures and longer cycle times. On the other hand, zinc die casting is usually more energy efficient, with its lower melting point and faster cycle times. Zinc Die Casting for Companies Looking to Go Green In the corporate world, more and more businesses are looking at the overall effect they have on the environment and the level of their carbon emissions. It makes ecological and economic sense: economically worthwhile because efficient use of energy saves money. In our pursuit of greener processes, the assessment and improvement of the energy utilizations in die-casting are always the key point for manufacturers who are looking for a balance between eco-friendliness and striking a balance between environmental responsibility and cost-effectiveness..
Application-Specific Considerations
Automotive Component Applications
For the automotive field, aluminum die castings are often chosen for engine blocks and transmission cases because they offer high strength and low weight. This combination is particularly advantageous in applications where increasing fuel economy and performance are dependent on the extent to which vehicle weight is minimized. Meanwhile, zinc die casting is a good method for parts that need complex designs and close tolerances, like small brackets and connectors. The decision between using aluminum or zinc on automobiles is determined by desired features and the trade-offs of each part.
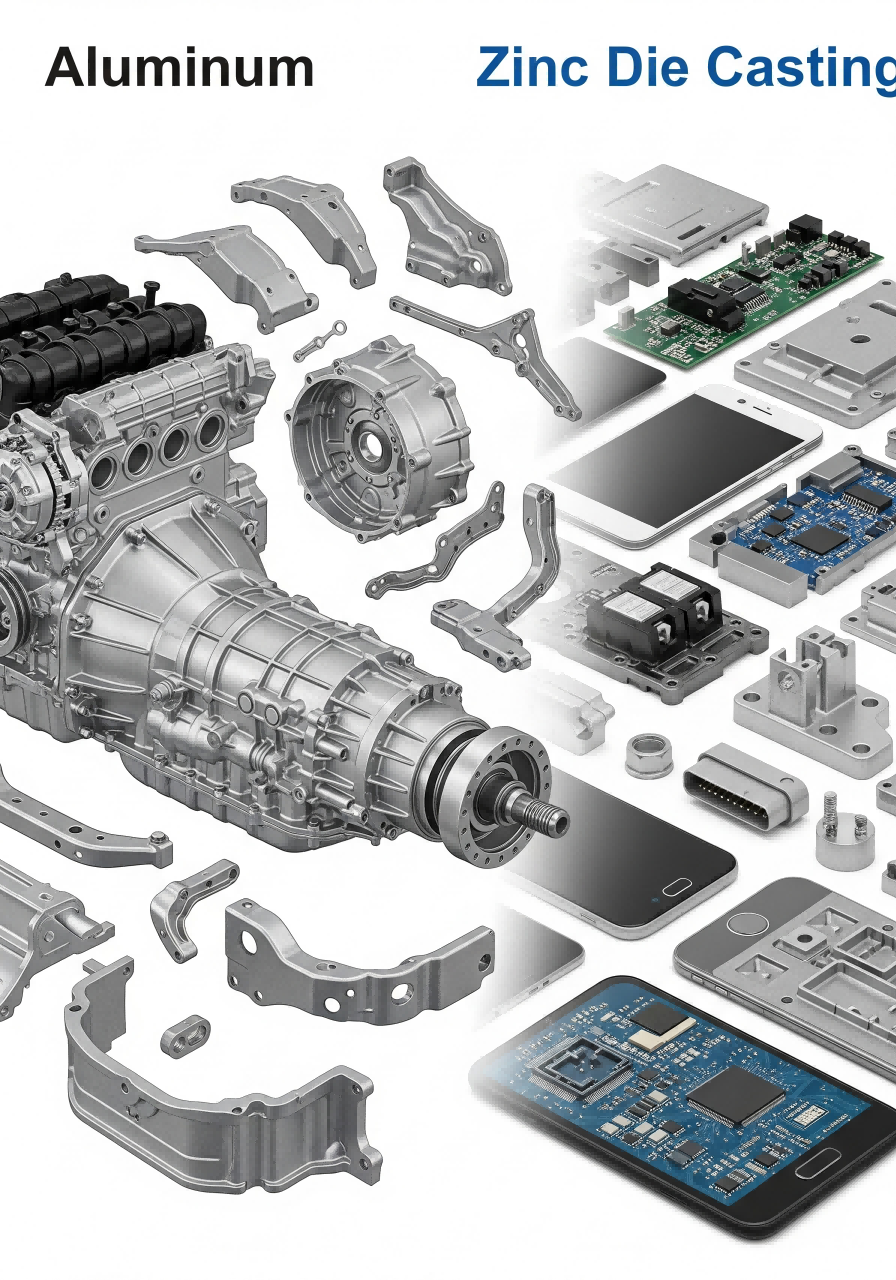
Electronics Housing Solutions
Electronic device housing also benefits from zinc in that it is superior in corrosion resistance and can be more precisely manufactured compared to plastic electronic casings. Its harsh environment survival capability and excellent resolution are second to none. While aluminum is an appropriate housing material, it may need further processing to meet operationally rigorous requirements. Manufacturers need to consider both the weight advantages of aluminum and the precision of zinc when it comes to electronic housing solutions.
High-Stress Industrial Parts
It’s the ideal material in high stress industries like defense and aerospace, due to its lightweight yet super strong profile. They are important characteristics in applications that require the overall weight to be minimized without sacrificing structural integrity. Zinc may be used for some industrial purposes, but its weakened strength typically prevents it from being used in high-stress applications. Key to selecting the right alloy to provide for both performance and longevity are stress profiles on parts.
Cost and Efficiency Evaluation
Tooling Costs Comparison
Tooling cost comparisons in zinc and aluminum reveal a cost disparity between high-performing, long-life aluminum tooling and the multi-manufacturing process's expensive production cycle tooling. While expensive to develop, aluminum tooling can justify it for larger production quantities, since its long life becomes cost competitive. In comparison to aluminum tooling, zinc tooling is typically more cost-effective for lower-volume productions. Hence, to evaluate the true cost of tooling over its life cycle, factors such as tool durability and production volume must be considered. It’s finding the right balance between all of them that’s key, especially in the long run for high-volume projects when it comes to aluminum tooling.
Long-Term Maintenance Factors
Die casting machines, whether used for aluminum or zinc die casting, need regular care and servicing to remain in operation and to ensure that quality parts are produced. Both do need maintenance, but aluminum machines require more because of excessive wear from the thermal cycling. Active investment in preventive maintenance can pay off quite well in terms of cost savings for the entire production life. Programs like these are generally comprised of regular inspections, lubrication, and replacing worn parts as needed to ensure reliable equipment and to avoid unplanned downtime. Emphasizing maintenance helps increase the performance of the machines and overall productivity in the long term.
Scalability for Mass Production
Aluminum die casting, due to the material properties, has potential for volume production due to the high-volume runs it can help high production needs economically. It also possesses excellent strength, and mass production can be performed at low cost due to aluminum's very good formability; therefore, it is suitable for industries that are targeted at mass production. On the other hand, although zinc die casting is also a scalable process, it has some drawbacks in relation to costs and also to production speed. For companies looking to expand, understanding the scale-up potential of each material allows for an informed decision-making process to choose a material that will best serve their manufacturing strategy and business as they grow.




