Alloy Melting Control and Impurity Management for Stable Microstructure
Getting good castings without defects really begins right at the melting furnace stage. When manufacturers keep tight control on what goes into the alloy mix, especially things like magnesium, silicon, and copper levels, they avoid those pesky grain problems down the line. Managing impurities matters a lot too. Keeping iron content under 0.15% helps prevent brittle parts from forming. Automated degassing processes bring hydrogen levels down to about 0.1 ml per 100 grams of aluminum, which is actually quite low compared to the 0.2 ml mark where porosity issues start getting serious (around 300% more pores!). The systems that remove slag during melting play their part as well, making sure the metal stays clean enough so the final product develops properly at a microscopic level.

Temperature & Pressure Synchronization Across Transfer, Shot, and Cooling Stages
Getting consistent results depends heavily on getting the right balance between heat and mechanics when working with metals during transfer, injection, and cooling stages. Keeping track of temperatures in real-time helps maintain melt temps around plus or minus 5 degrees Celsius during transfer, which stops things from solidifying too early and prevents those pesky oxide layers from forming. When injecting material into molds, adjusting pressure based on what the mold looks like allows for smoother fills without turbulence at speeds typically ranging from 40 to 100 meters per second. This matters a lot because it keeps air bubbles out and makes sure parts come out dimensionally correct. After the mold is filled, controlling how fast things cool down becomes crucial too. For aluminum components, cooling rates usually sit somewhere between 10 and 15 degrees Celsius per second. This careful cooling affects grain structure, cuts down on internal voids, and reduces stress buildup inside the part. According to actual factory statistics we've seen across various plants, when pressure and temperature settings work together properly, cold shuts drop by about 70 percent. That's why most serious manufacturers invest in systems that tie all these factors together rather than treating them as separate concerns.
| Stage | Critical Parameters | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Transfer | Melt temp (±5°C), transfer speed | Prevents cold shuts, oxide formation |
| Shot | Injection pressure (800–1000 bar), speed | Eliminates air entrapment, ensures dimensional accuracy |
| Cooling | Cooling rate, time | Controls grain size, reduces porosity |
This multi-stage synchronization is pivotal for minimizing dimensional drift in high-volume production.
Integrated In-Line Inspection: From First Article to Final Release
Maintaining consistent quality in high-volume die-casting production demands rigorous inspection protocols embedded directly into the manufacturing workflow—catching deviations early and preventing costly defects from propagating downstream.
ISO 9001–Aligned Sampling Protocols (First-Article, Patrol, Final) in High-Volume Die Casting Factory Workflow
Meeting ISO 9001 standards means implementing several layers of quality checks throughout production. First Article Inspections (FAI) check everything from tools to raw materials and process settings right before starting full-scale manufacturing. These inspections compare what comes out of the mold to exactly what was designed on paper. Then there are regular patrols during production runs. These happen at set times to measure important parts and test materials after they've been trimmed or heat-treated, catching any subtle changes in how things are being made. When it comes time to ship products, final inspections make sure each batch looks good, works properly, and matches all the required measurements. This whole system creates records we can track back through and gives us solid data about product consistency across batches. Best part? It doesn't slow down our overall production speed too much while still keeping quality high.

Operator-Led Real-Time Checks: Release Agent Application, Flash Detection, and Mold Condition Monitoring
Giving operators hands-on monitoring duties creates something no machine can replace when it comes to stopping defects before they happen. Before starting each production run, these folks check if the release agent is applied evenly across all surfaces, which stops parts from sticking and avoids those annoying surface blemishes. When parts get ejected from the mold, experienced workers spot excessive flash right away, something that usually means either the mold is wearing out or there's not enough clamping pressure holding everything together. While waiting between production cycles, operators compare what the temperature sensors are saying against what they actually see happening on the mold itself, looking for signs of wear or damage so maintenance crews know where to focus their efforts. Human eyes catch those tiny changes in the process that automation simply misses sometimes. Things like gradual shifts in heat distribution or slow breakdown of hydraulic components get noticed early, preventing issues like porous parts, cold shuts, and all sorts of dimensional problems down the line.

Root-Cause-Driven Defect Prevention: Cold Shut, Porosity, and Warping
In high-volume die casting, addressing defects like cold shut, porosity, and warping demands a systematic, root-cause approach—not reactive rework. Thermal analysis, simulation validation, and closed-loop feedback form the backbone of proactive quality assurance.
Thermal Mapping + Mold Preheating Correlation for Cold Shut and Cracking Mitigation
Cold shuts happen when molten metal doesn't properly fuse together because parts of the mold get too cool or there's temperature imbalance across the mold surface. Thermal mapping with those infrared sensors lets manufacturers see exactly how heat is distributed throughout the process. When they match this information with proper mold preheating steps, it cuts down on cold shut problems by around 40 percent according to recent studies. Keeping mold surfaces consistently warm (above 200 degrees Celsius) while the metal flows into place makes everything work better and reduces cracks caused by sudden temperature changes. The ability to tweak settings in real time based on these thermal readings keeps things running smoothly even during fast production cycles where maintaining stable temperatures remains a constant headache for plant operators.
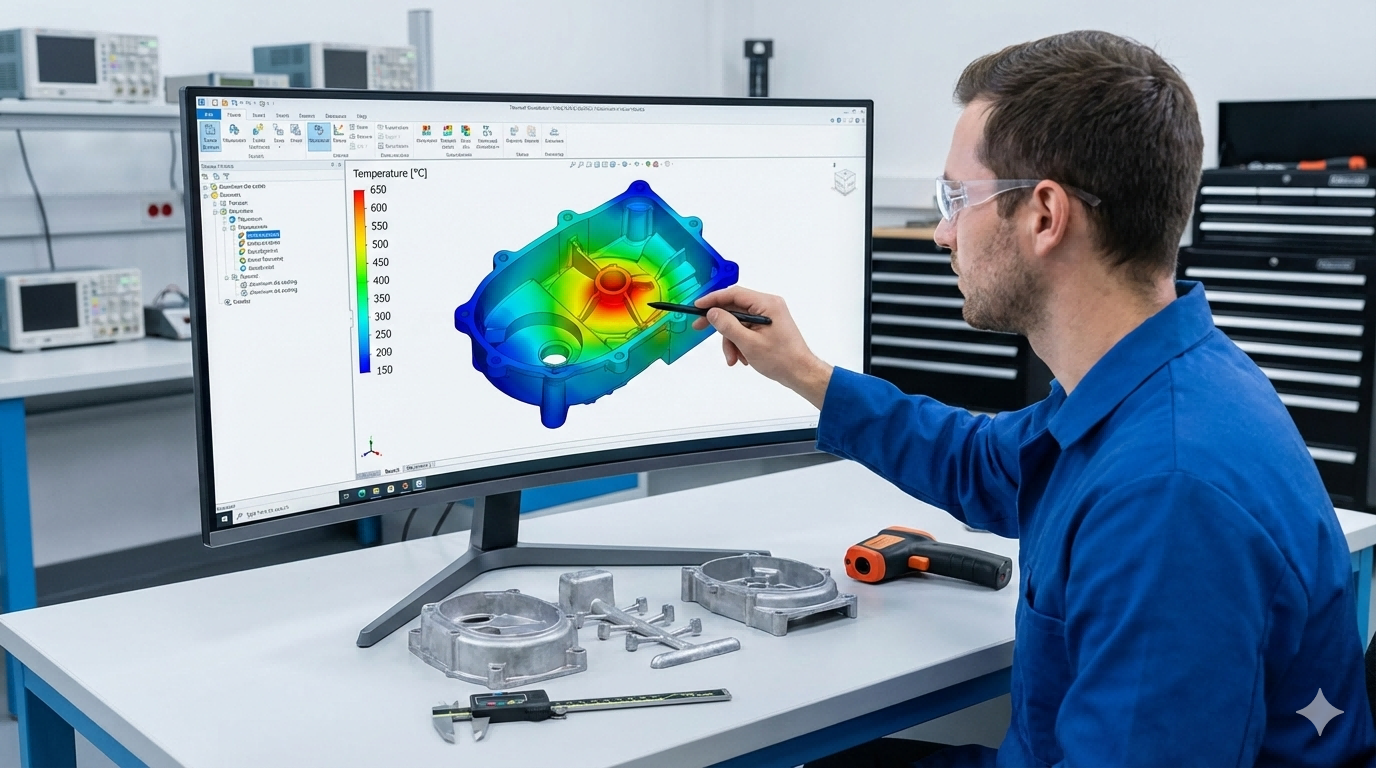

Simulation-Validated Parameter Standardization to Reduce Porosity and Dimensional Drift
Porosity happens when gases get trapped or when there are shrinkage related voids as materials solidify, which weakens structures and makes dimensions unstable. Using advanced simulation tools helps check standard injection pressures, how fast things cool down, and gate design before actual manufacturing starts. This approach can reduce porosity issues by around 30 percent according to industry data. Digital twin technology works on improving how air escapes and how molten material flows through molds, encouraging proper solidification patterns and better metal distribution throughout parts. Combine this with closed loop monitoring systems and sensors that provide instant feedback, manufacturers can adjust cooling processes within milliseconds. Such rapid response prevents those pesky internal voids and warping problems that often occur because heat doesn't escape evenly across different sections of cast components.
Technology-Enabled Accountability: NDT, Automation, and Closed-Loop QA Systems
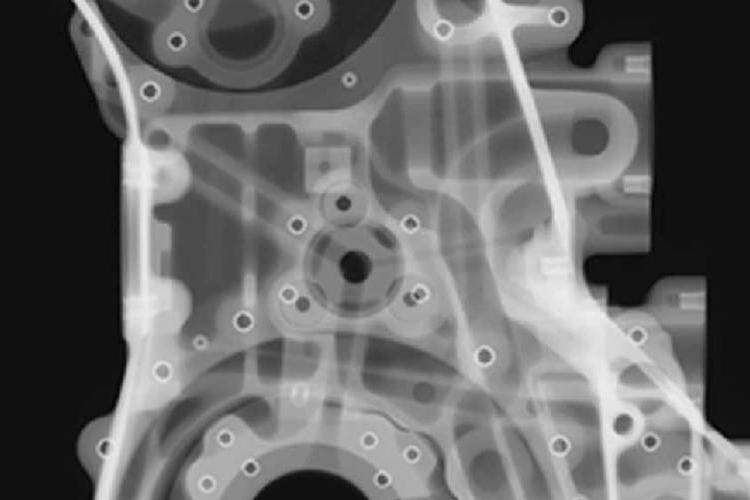
Today's die casting plants have moved beyond simple inspections when it comes to quality control. They actually integrate various technologies throughout their operations. For instance, automated X-ray and CT scans check every single item in large production batches for problems inside the metal such as tiny air pockets. This covers all products instead of just samples, which was common with older manual checks. The quality assurance systems work in loops too. When inspectors find something wrong during real-time checks, this information gets sent right back to the casting machines. The machines then tweak things like how hard they push molten metal into molds within half a second or so. This quick response cuts down on defects by around half to three quarters compared to what used to happen before these systems were put in place. Special lasers measure dimensions down to fractions of a millimeter as parts come out of the machine. At the same time, smart computer programs look at past performance records of molds to figure out when maintenance might be needed before any actual breakdown happens. All these tech solutions help manufacturers meet those tough requirements set by car makers and aircraft companies for millions of cast parts each year. What used to be a stop and start process has become something that constantly adjusts itself during production.
FAQ
What is the importance of controlling alloy composition in die casting?
Controlling alloy composition—including elements like magnesium, silicon, and copper—is crucial as it helps prevent grain problems and defects in the final product. Managing impurity levels, such as keeping iron content low, ensures the structural integrity of the casting.
How does thermal distribution impact the die casting process?
Thermal distribution is vital for ensuring molten metal properly fills the mold without cooling too quickly, which can lead to cold shuts and cracks. Proper thermal mapping and preheating of molds ensure consistent temperature surfaces, improving fusion and reducing defects.
What role do inspections play in high-volume die casting production?
Inspections are embedded in the workflow to catch deviations early, preventing defects from propagating. This includes First Article Inspections, patrol inspections during production, and final checks prior to shipping, aligned with ISO 9001 standards.
How is technology enhancing quality control in die casting?
Technology—including automated X-ray, CT scans, and real-time adjustments—ensures all parts are checked for defects. Closed-loop systems provide immediate feedback for adjustments, cutting down defects significantly and meeting stringent industry standards.




