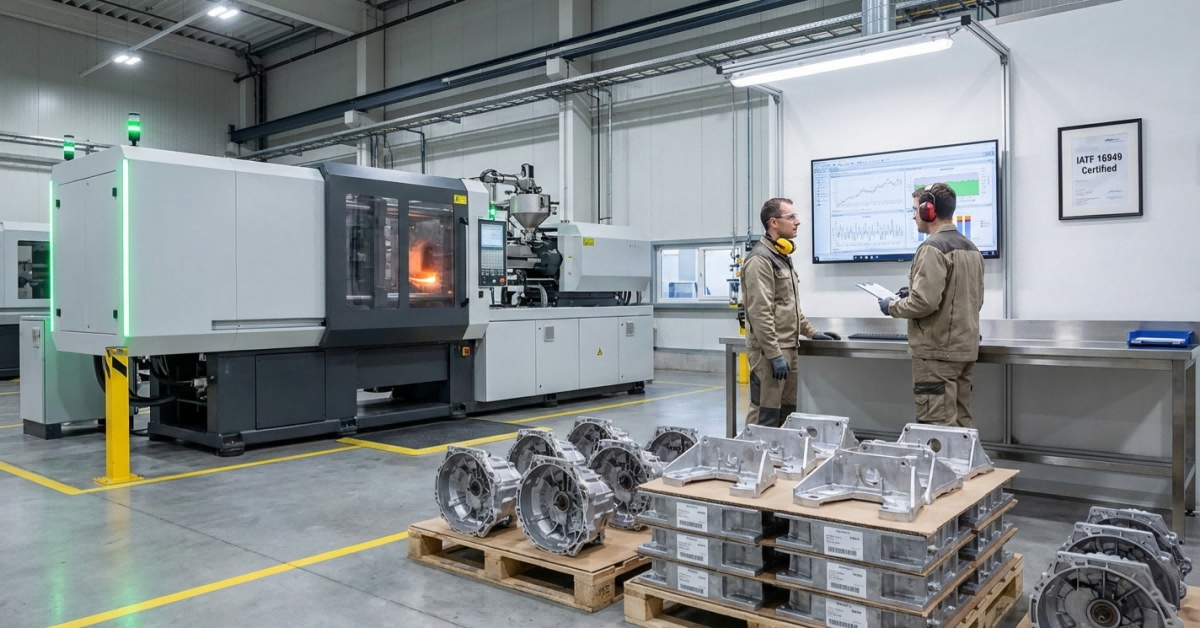
IATF 16949 Foundations: Process Discipline as the Bedrock of Die Casting Reliability
Systematic Control of High-Pressure Die Casting Parameters (Temperature, Shot Speed, Cycle Time)
The IATF 16949 standard requires strict process controls for high pressure die casting operations, focusing on real time management of key factors throughout production. Keeping melt and die temperatures stable is crucial for maintaining proper alloy flow characteristics and avoiding early solidification issues. Shot speed needs careful calibration too since it directly affects how metal flows into intricate mold cavities during filling. Cycle times must also be balanced properly between production output goals and sufficient cooling periods to reduce stress buildup and shape distortions. Modern monitoring equipment tracks all these parameters every two seconds or so, automatically alerting operators whenever readings drift beyond acceptable ranges, typically around plus or minus three percent. According to industry data from automotive manufacturers, following these guidelines cuts down on dimensional inconsistencies by roughly forty one percent when compared with plants that don't have certification. Every six months or thereabouts, companies conduct detailed capability assessments using techniques like CpK analysis along with various other statistical tools to check whether their processes remain consistently within spec over multiple production batches.
Preventing Common Defects—Porosity, Cold Shuts, and Flash—Through IATF 16949’s Preventive Action Requirements
The IATF 16949 standard has developed a framework for preventive actions that focuses on finding and fixing the root causes behind common die casting defects before problems actually happen. When it comes to porosity issues, manufacturers often turn to vacuum assisted casting systems which keep chamber pressures under 50 millibar so trapped air gets removed from the mix. For cold shut problems, companies combine specially formulated alloys with gate speeds around or above 40 meters per second to make sure metal fronts merge properly during casting. Flash control requires regular die maintenance along with careful adjustment of clamp forces staying within about plus or minus 5 percent of what materials need. Regular audits check whether all these control measures are being followed correctly across different production stages. And when something goes wrong repeatedly, there's a formal process to investigate why it keeps happening. Many automotive parts suppliers have seen their scrap rates drop by roughly two thirds after fully adopting IATF 16949's prevention approach, according to industry reports. This kind of improvement makes a real difference in both quality control and bottom line savings over time.
Traceability and Risk-Based Thinking: Core IATF 16949 Drivers of Consistent Reliability
Material Genealogy and Real-Time Process Traceability from Alloy Ingot to Finished Component
The IATF 16949 standard demands complete traceability across every stage of production starting from when alloy ingots arrive at the facility all the way through melting processes, casting operations, heat treatments, and final finishing steps. This comprehensive tracking helps prevent contamination issues that can lead to problems like porosity or material embrittlement. With real time monitoring systems in place, manufacturers can check critical process parameters such as cavity pressures during casting, how fast things cool down after heating, and overall temperature profiles throughout manufacturing. Each individual part gets linked back to exactly what happened during its creation journey. According to recent findings published by SAE International in their 2023 industry benchmark report, companies that adopt these full circle traceability practices see about a 41% reduction in defects causing product failures.

FMEA-Driven Mitigation of Reliability Risks: Shrinkage, Dimensional Instability, and Interfacial Defects
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is central to IATF 16949’s risk-based approach, requiring cross-functional teams to systematically assess severity, occurrence, and detection of reliability threats like thermal shrinkage, dimensional drift, and interfacial weaknesses. Mitigation actions are validated—not assumed—and embedded into process controls.

| Reliability Risk | FMEA-Driven Mitigation | Validation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Shrinkage defects | Optimized cooling curve controls | Thermal simulation + CT scanning |
| Dimensional drift | In-die monitoring + SPC limits | First/last piece audits |
| Interfacial weaknesses | Alloy purity protocols + flux checks | Microsection analysis |
This evidence-based methodology prevents field failures by resolving root causes before volume production begins.
Validated Reliability Outcomes: How IATF 16949 Certification Translates to Automotive-Specific Performance
Field Data from Certified Tier-1 Suppliers: 32% Average Reduction in Warranty Claims for Structural Die Castings
IATF 16949 quality standards have definitely made a big difference in how reliable die castings are for cars. Most Tier-1 suppliers who get certified see their field failure rates drop significantly, especially when it comes to those critical parts where safety matters most. Think about engine mounts, those suspension knuckles that take all the punishment, and cross members holding everything together. According to industry reports, certified plants typically experience around 32% fewer warranty claims for structural castings. Why does this happen? Well, the standard focuses heavily on stopping problems before they occur, thoroughly testing processes, and keeping tabs on operations constantly. Certified manufacturers tackle common issues head-on like porosity in materials, parts that don't stay dimensionally stable over time, or heat treatments that aren't consistent across batches. What we end up with are components built to handle what automotive environments throw at them day after day. Fewer parts need replacing early on, which saves money for car makers in the long run while also improving both safety and how long things last. Looking at how much better warranty records look for certified facilities tells us something important about IATF 16949's impact on making mission-critical castings truly dependable over time.

FAQ
Q: What is the main benefit of IATF 16949 in die casting?
A: The main benefit is a significant reduction in defects and improved reliability of die cast components by implementing strict process controls and preventive actions.
Q: How does IATF 16949 help in preventing common die casting defects?
A: By focusing on root cause analysis and corrective actions for defects like porosity, cold shuts, and flashes, IATF 16949 helps prevent these issues before they occur.
Q: What role does traceability play in IATF 16949?
A: Complete traceability from alloy ingot to finished product ensures quality control and helps prevent contamination issues that could lead to defects.
Q: How does FMEA contribute to IATF 16949's goals?
A: FMEA evaluates potential risks in manufacturing processes and drives the implementation of mitigation actions to prevent failures before production begins.
Q: What improvements do certified manufacturers experience with IATF 16949?
A: Certified manufacturers typically see a significant reduction in warranty claims and defects, leading to cost savings and improved safety and durability of their products.




