Understanding the Root Causes of Key Challenges in Aluminum Die Casting
Common Defects and Failures in Aluminum Die Casting Processes
Porosity continues to be the biggest headache for aluminum die casters, with industry data suggesting it affects somewhere around 15 to 20 percent of all production batches as per a recent 2023 survey among foundries. What makes things worse is that porosity often shows up alongside other problems like hot tearing when parts can't contract properly during solidification, plus those pesky shrinkage cavities that form because different areas cool at different rates. There are plenty of other common defects too - think surface blisters caused by leftover mold release agents getting trapped inside, or cold shuts where molten metal doesn't merge correctly because it wasn't flowing fast enough. Factory floor reports indicate roughly a third of all defective material comes down to bad vent design or when they pour metal above about 680 degrees Celsius, temperatures that really kickstart oxide formation on the metal surfaces.
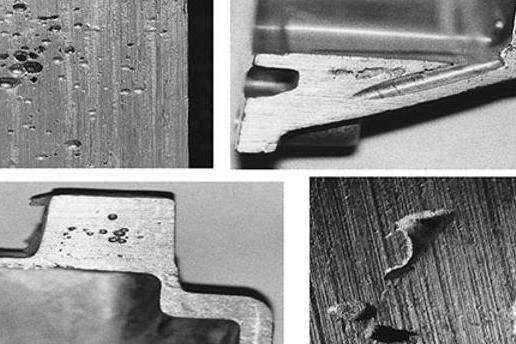
Scientific Principles Behind Porosity, Cracking, and Shrinkage
Three physical phenomena drive these defects:
- Gas entrapment: Dissolved hydrogen (up to 0.3 mL/100g in AlSi9Cu3 alloys) nucleates bubbles during solidification
- Thermal stress: Coefficient differences between mold (1.2×10−³ K° for H13 steel) and casting (2.3×10−³ K° for Al) create crack-initiating stresses
- Shrinkage compensation failure: 6–7% volumetric contraction during cooling requires precise pressure control within 50–100 MPa ranges
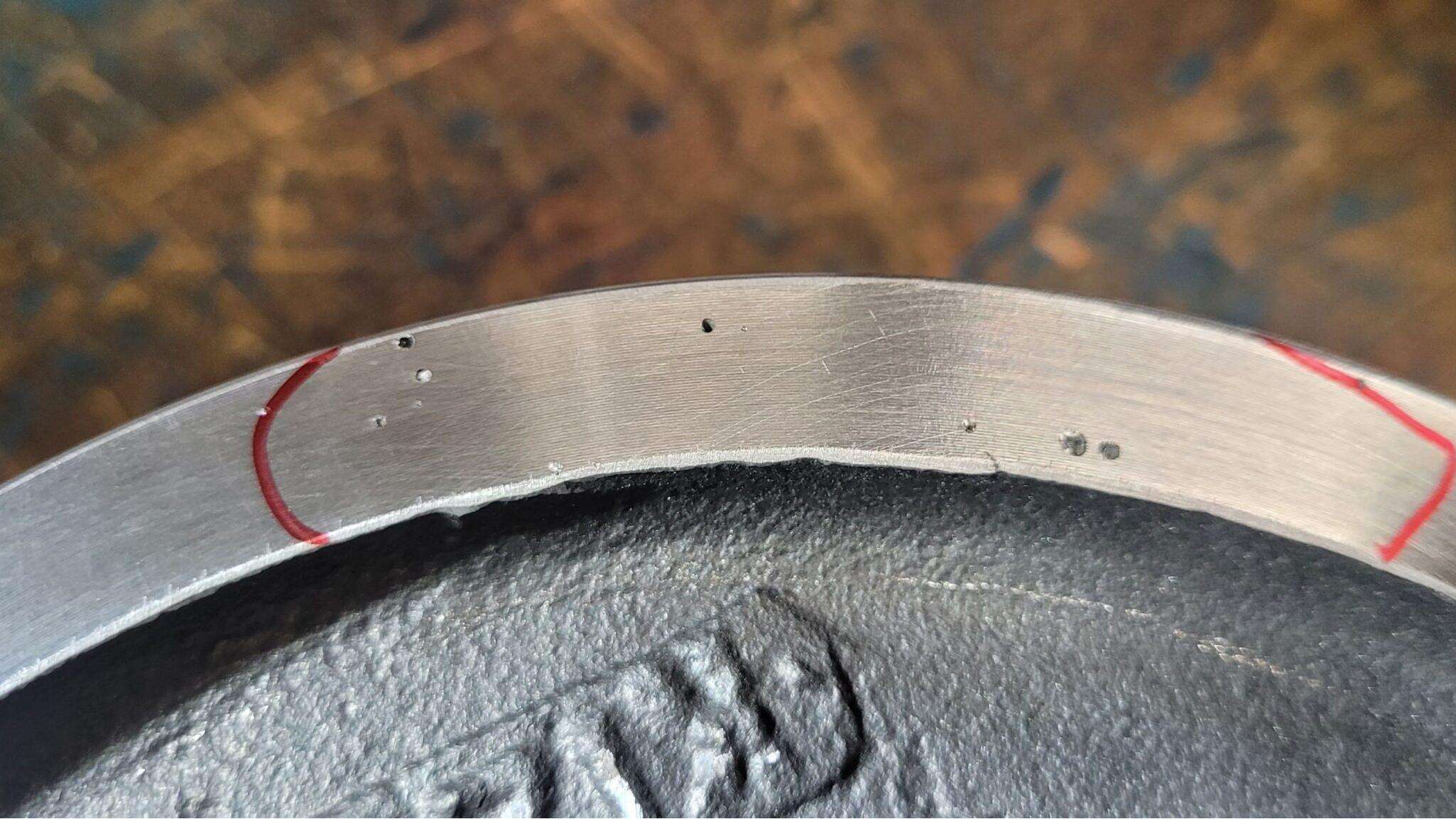

Case Study: Analyzing Defects in Automotive Aluminum Components
A 2024 analysis of 50,000 automotive transmission housings revealed critical patterns:
| Defect Type | Frequency | Primary Root Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Microporosity | 62% | Inadequate vacuum levels (<80 kPa) during HPDC |
| Hot tears | 28% | Uneven die temperatures (±15°C across zones) |
| Dimensional variation | 10% | Insufficient clamping force (below 2,500 tons) |
| Implementing real-time pressure sensors and AI-driven cooling optimization reduced scrap rates from 18% to 4.7% within eight production cycles. |
Combating Porosity and Gas Entrapment with Advanced Process Control
Mechanisms of Pore Formation and Gas Trapping During Solidification
The pores that show up in aluminum die castings come mainly from two places. First there's the hydrogen gas that gets mixed into the melted aluminum. Then we have air getting trapped when the metal is injected into molds. When the metal starts cooling down, the amount of hydrogen that can stay dissolved plummets around 90 percent, which causes those tiny bubbles to form. At the same time, if the metal flows too roughly through the mold, it catches little pockets of air, especially in parts with complicated shapes. These air pockets can grow quite large actually, sometimes taking up over 5% of the whole part's volume when things go really wrong during production.
Role of Vacuum Die Casting (HVDC) in Reducing Internal Defects
High Vacuum Die Casting or HVDC as it's often called cuts down on gas bubbles in cast parts because the chamber stays at around 50 to 80 millibar pressure when molten metal gets injected into the mold. That pressure level is about 95 percent less than what traditional casting methods use. The vacuum helps push out a lot of trapped air too, somewhere between 60 and 75 percent reduction actually. And this isn't just good for quality control either since the process allows for better filling speeds without compromising integrity. Some recent tests looked at how well this works for making car transmission cases. Before switching to HVDC, factories were throwing away about 12 out of every 100 parts after machining them. After implementing the new tech, those waste rates dropped all the way down to just 3.8%. These findings appeared last year in the Journal of Materials Processing Technology by the way.
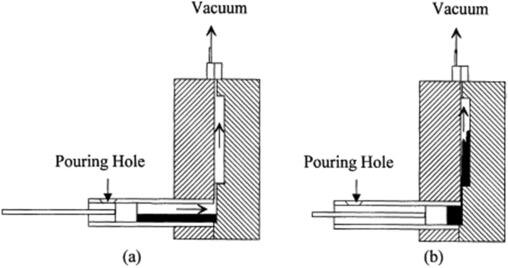
Real-Time Monitoring and Process Optimization Strategies
Modern systems employ three synchronized controls to prevent defects:
| Parameter | Monitoring Tool | Adjustment Range |
|---|---|---|
| Molten metal temp | Infrared pyrometers | ±5°C stabilization |
| Injection velocity | Servo-controlled pumps | 0.5-8 m/s modulation |
| Vacuum levels | Pressure transducers | 20-100 mbar regulation |
Closed-loop algorithms adjust variables within 30ms of detecting viscosity changes or gas pockets, achieving 99.2% dimensional consistency in high-volume production.
Extending Die Lifespan by Managing Thermal Fatigue and Wear
Impact of Cyclic Thermal Stress on Mold Durability
The constant heating and cooling that happens during aluminum die casting makes the tool steel expand then shrink again, which builds up stress points over time and speeds up wear and tear on the equipment. According to research published by the Ponemon Institute last year, when dies fail early because of this issue, companies end up losing around $740,000 every year just from unexpected shutdowns. Most often, cracks start forming right at those tricky spots like sharp edges or thinner parts of the mold where temperature control is hardest to maintain consistently across different production runs.
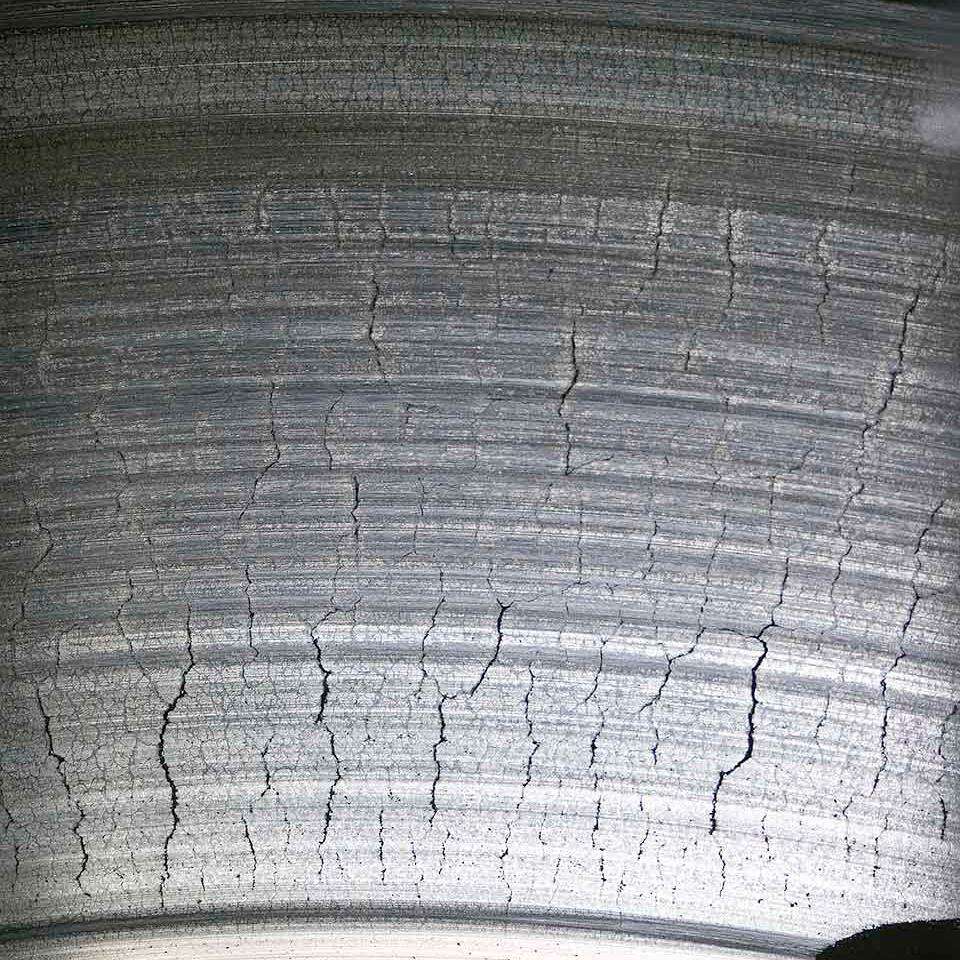

Optimal Tool Steel Selection and Surface Treatment Techniques
High-grade tool steels with 5–10% chromium content demonstrate 35% better thermal fatigue resistance than standard grades according to material testing. Advanced surface treatments like plasma nitriding reduce adhesion of molten aluminum while increasing surface hardness to 1,200+ HV. Manufacturers combining these techniques report 28% longer service intervals compared to untreated dies.
Case Study: Enhancing Mold Life Through Coatings and Heat Treatment
A tier-1 automotive supplier extended core pin lifespan by 40% using a hybrid approach:
- Applying CrN PVD coatings to sliding components
- Implementing cryogenic treatment (-196°C) before final tempering
- Introducing conformal cooling channels within die inserts
This three-pronged solution maintained dimensional stability through 120,000 casting cycles under 700°C operating conditions.
Preventive Maintenance and Replacement Scheduling for Dies
Leading foundries employ predictive analytics to optimize die replacement timing:
| Parameter | Monitoring Method | Action Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Erosion | 3D profilometry | >0.25mm depth |
| Crack Propagation | Dye penetrant testing | >2mm length |
| Dimensional Shift | CMM measurement | ±0.15mm tolerance |
Scheduled replacements based on these metrics reduce unplanned downtime by 35% while maintaining casting quality within ISO 9001 specifications.
Optimizing Part Design and Manufacturing Feasibility in Aluminum Die Casting
Design for Manufacturing: Draft Angles, Fillets, and Parting Lines
Critical geometric features like 1–3° draft angles enable smooth mold release, reducing scrap rates by up to 18% in high-volume aluminum die casting (Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2023). Strategic placement of radii (minimum 0.5mm) at intersections minimizes stress concentration, while properly aligned parting lines prevent flash formation and secondary machining costs.
Incorporating Functional Features Without Sacrificing Integrity
Balancing functional requirements with manufacturability requires careful wall thickness control (2.5–4mm optimal range for most automotive components). A 2023 thermal analysis study demonstrated how integrated cooling channels in cast electronics housings improved heat dissipation by 40% without compromising structural rigidity through topology-optimized rib patterns.
Leveraging Simulation Tools for Complex Geometry Optimization
Modern aluminum die casting simulations now predict fill patterns with 92% accuracy, enabling engineers to optimize runner systems and gate locations before tooling fabrication. This technology reduced porosity defects by 30% in a recent aerospace component project through virtual validation of vacuum-assisted casting parameters (Materials & Design, 2024).
Key Process Considerations:
- Wall Thickness Tolerance: ±0.25mm achievable with premium tooling
- Simulation ROI: $3–5 saved per part in defect reduction for batches over 10k units
- Critical Angles: >90° internal corners require adaptive core designs

Ensuring Consistent Quality and Cost-Effective Production
Defect Detection and Root Cause Analysis in High-Volume Casting
Modern aluminum die casting operations deploy automated X-ray inspection systems to detect subsurface porosity in 98% of cases (NIST, 2023). These systems combine machine learning algorithms with real-time defect mapping, enabling engineers to trace issues like gas entrapment back to specific process parameters such as melt temperature fluctuations or insufficient venting.
Balancing Production Speed with Quality Control Demands
Statistical process control (SPC) methods reduce scrap rates by 25–40% while maintaining cycle times below 90 seconds for automotive components. Critical parameters like die temperature (±5°C variance) and injection velocity (4–6 m/s) are monitored through IoT-enabled sensors, ensuring quality benchmarks aren’t compromised for throughput gains.
Reducing Long-Term Costs Through DFM and Process Simulation
Advanced Design for Manufacturing (DFM) software cuts prototyping iterations by 60% by simulating mold filling patterns and thermal stresses. A 2023 study showed manufacturers using these tools reduced per-part costs by 18% through optimized runner designs and minimized material overflows during solidification.
FAQs on Aluminum Die Casting
What are the main causes of porosity in aluminum die casting?
Porosity in aluminum die casting is mainly caused by gas entrapment involving dissolved hydrogen and air traps during molding processes.
How does Vacuum Die Casting help reduce casting defects?
Vacuum Die Casting helps minimize defects by significantly reducing the amount of trapped air and gas bubbles through lower pressure in the mold, leading to better part integrity and reduced waste.
What are some methods to extend the lifespan of casting dies?
Methods such as using high-grade tool steels, surface treatments like plasma nitriding, and implementing predictive maintenance with monitoring tools can extend die lifespan by managing thermal fatigue and wear.
How can simulation tools aid in aluminum die casting?
Simulation tools can predict fill patterns and optimize runner systems and gate locations, reducing defect rates and prototyping iterations while ensuring better design feasibility and cost savings.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Root Causes of Key Challenges in Aluminum Die Casting
- Combating Porosity and Gas Entrapment with Advanced Process Control
- Extending Die Lifespan by Managing Thermal Fatigue and Wear
- Optimizing Part Design and Manufacturing Feasibility in Aluminum Die Casting
- Ensuring Consistent Quality and Cost-Effective Production
- FAQs on Aluminum Die Casting




