ISO 9001: The Foundation of Quality Management in Die Casting Factories
Understanding the role of ISO 9001 in die casting factory operations
Getting ISO 9001 certified means implementing a quality management system that helps die casting plants follow international standards for making their processes better and preventing defects. The certification requires companies to document how things get done around the shop, set up plans for fixing problems when they happen, and keep records of worker training sessions. All this paper work actually makes people responsible throughout the whole manufacturing chain. Take one medium sized aluminum die caster as an example they saw their porosity issues drop by almost 60 percent after about a year and half since getting certified thanks to tighter control over their production methods according to research published in Materials Engineering Journal last year.

How ISO 9001 ensures process consistency and quality control through standardized workflows
Manufacturing standards require detailed records of melt temps, die fill pressures, and how fast things cool down after casting. When companies follow these rules closely, they see a big difference in quality control. Factories that are properly certified tend to produce parts with about 60 percent fewer size problems than those without certification. Most shops now have some sort of real time tracking system watching over their machines. These systems keep tabs on how long each cycle takes and count defects as they happen, so operators can tweak settings mid production when something starts going wrong.
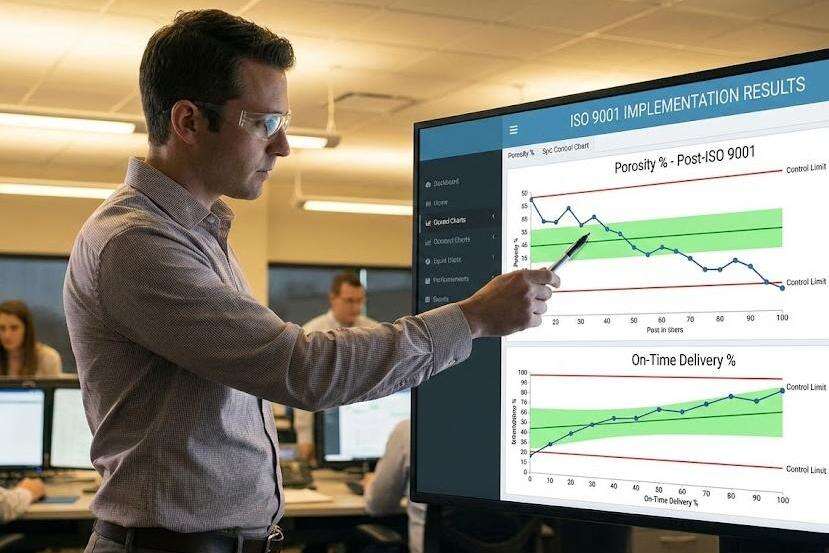
Case study: Improved defect rates after ISO 9001 implementation in a mid-sized aluminum die casting factory
| Metric | Pre-ISO 9001 | Post-ISO 9001 | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average porosity rate | 5.8% | 2.4% | 58.6% |
| On-time delivery | 72% | 94% | 22% |
| Customer return rate | 14% | 3% | 78.5% |
The foundry achieved these results by implementing standardized tooling maintenance schedules and Statistical Process Control (SPC) protocols required under ISO 9001 guidelines.
Linking ISO 9001 to customer satisfaction and repeat business in precision parts manufacturing
Manufacturers requiring tight-tolerance components (±0.05mm) increasingly prioritize ISO-certified suppliers, with 83% citing reduced inspection costs as a key benefit (Precision Manufacturing Survey, 2024). Certified die casting factories typically demonstrate 40% higher repeat order rates due to improved First-Time Yield (FTY) metrics and traceable quality documentation.
IATF 16949: Ensuring Automotive-Grade Compliance for Die Casting Suppliers
Why IATF 16949 is Essential for Automotive and EV Supply Chain Partnerships
For the automotive sector, getting IATF 16949 certified basically means business as usual when it comes to quality control standards, especially important for those die casters making parts for electric vehicles. The numbers tell the story too - McKinsey predicts EV manufacturing will jump by about 35 percent each year all the way till 2030. So what does this mean? Well, having that IATF 16949 stamp shows suppliers can actually handle those tough demands around preventing defects and keeping track of everything properly. Car makers themselves insist on seeing this compliance because they need to cut down on risks, particularly for components that matter most to safety. Think about things like housing units for batteries or those motor mounts. If any of these fail, we're talking massive recalls and serious headaches for everyone involved.

How IATF 16949 Enhances ISO 9001 With Risk Management, Traceability, and Defect Prevention
The IATF 16949 standard builds upon the basics of ISO 9001 but goes much further when it comes to analyzing possible failures and keeping tabs on processes as they happen. When die casting plants get certified under this system, they start thinking about risks ahead of time so they can spot problems before they become actual defects. These facilities track materials at every stage from when the metal is melted all the way through to the final product being made. They also put in place special controls that cut down on scrap caused by air pockets in the castings, sometimes reducing waste by around 25%. For automotive parts suppliers, getting through the Production Part Approval Process takes about 40% less time compared to companies without these certifications, which makes a big difference in meeting tight deadlines and staying competitive in the market.
Trend Analysis: Rising Demand for IATF 16949-Certified Die Casting Factories in Electric Vehicle Production
Most electric vehicle makers are pushing for IATF 16949 certification on nearly all their new supplier deals when it comes to structural castings according to Ducker Carlisle's latest research from 2024. The reason? Modern cars need parts made to incredibly tight specs. Battery trays must fit within fractions of a millimeter tolerance, while high pressure die casting operations can't afford even a single defect. Factories also need to work smoothly with digital quality tracking systems across their production lines. Suppliers who get certified typically see their project approvals come through about a quarter faster than those sticking with just ISO 9001 standards. This speed difference matters a lot when companies are racing to bring new EV models to market ahead of competitors.
Strategy: Validating Supplier Compliance Through IATF 16949 Documentation and Process Audits
Effective certification verification requires:
| Audit Focus Area | Critical Checks for Die Casting Suppliers |
|---|---|
| Process Validation | Review of DOE (Design of Experiments) for gating systems |
| Material Traceability | Audit trail from alloy certificates to heat-treat logs |
| Corrective Actions | Analysis of 8D reports for porosity defects |
Leading procurement teams combine documentation reviews with on-site audits of die casting cell process capability indices (Cpk ≥1.67), ensuring suppliers meet automotive-grade quality thresholds consistently.
NADCA Certification: Advancing Technical Excellence in Aluminum and Zinc Die Casting
How NADCA Sets Industry Benchmarks for Surface Finish, Porosity Control, and Dimensional Accuracy
The North American Die Casting Association (NADCA) establishes quantifiable thresholds for critical parameters like surface roughness (<3.2 μ Ra) and porosity rates (<1.2% by volume) in aluminum and zinc die casting. These standards align with 78% of aerospace and medical OEM specifications, ensuring components meet tolerance limits as tight as ±0.05 mm.
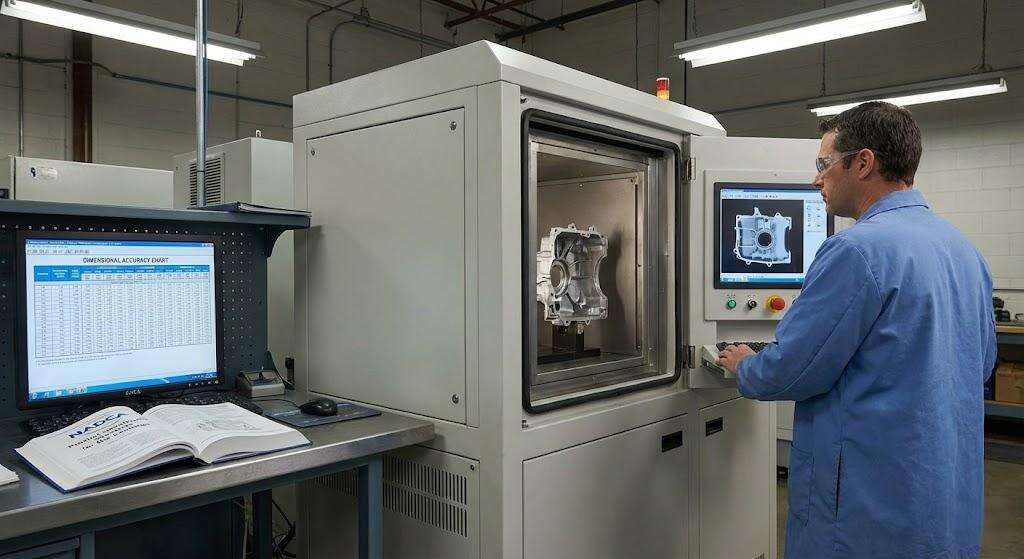

Verifying Technical Capabilities: What NADCA Certification Reveals About a Die Casting Factory’s Proficiency
NADCA-certified facilities demonstrate validated capabilities in thermal management systems that prevent premature die degradation, real-time X-ray inspection for sub-surface defects, and process controls maintaining melt temperature within ±5°C. A 2023 audit of 47 suppliers found NADCA-certified factories reduced dimensional non-conformities by 62% compared to uncertified peers.
Case Study: Performance Comparison Between NADCA-Certified and Non-Certified Zinc Die Casting Suppliers
A two-year automotive latch component study (2022–2024) revealed:
| Metric | NADCA-Certified Suppliers | Non-Certified Suppliers |
|---|---|---|
| Defect Rate | 0.8% | 4.1% |
| Tool Life Extension | +35% | Baseline |
| Surface Rework Costs | $18k/month | $74k/month |
Certified suppliers achieved 98.2% first-pass yield through NADCA-compliant die lubrication protocols.
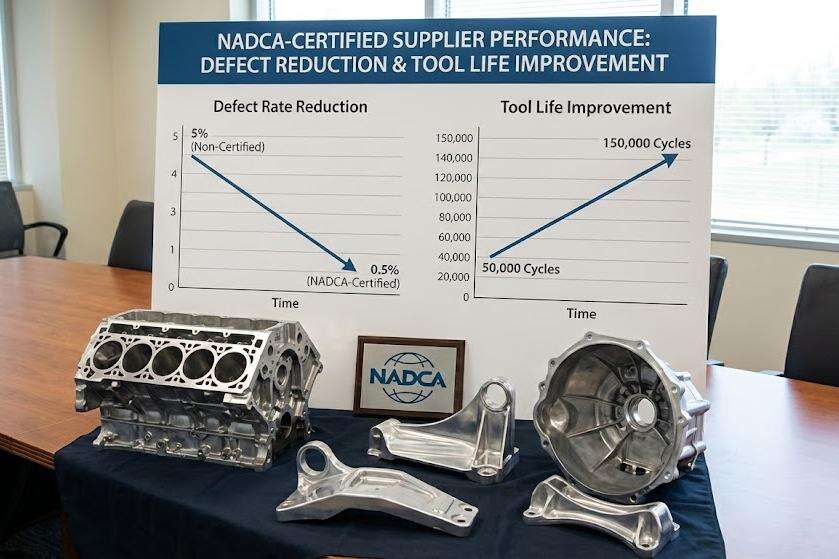

Market Trend: Growing Buyer Preference for NADCA-Certified Partners in High-Integrity Casting Applications
87% of EV battery housing buyers now mandate NADCA certification in RFQs, per a 2024 die casting industry report. This aligns with OEM demands for leak-proof tolerances (<0.1% porosity) in structural components subjected to 20+ MPa pressures.
Material-Specific Accreditations: ASTM, MIL-STD, and Their Role in High-Performance Die Casting
Why Material Certifications Matter for Reliability in Aerospace, Defense, and Medical Die Casting
Certifications for materials are really important safety nets in sectors where parts failing just won't cut it. Take an aerospace actuator manufacturer for instance they need to prove their aluminum alloys have absolutely no porosity when subjected to intense pressure testing. Medical equipment makers meanwhile demand complete tracking records for every batch of zinc alloy going into those special housings that work safely inside MRI machines. Regular quality control simply doesn't catch what these certifications uncover. Looking back at some recent problems in military supply chains, researchers discovered last year that nearly two thirds of all failures traced back to using materials without proper certification during the die casting process.
ASTM B85 and MIL-STD Standards for Aluminum Alloy Integrity and Mechanical Performance
The ASTM B85 standard basically checks if aluminum alloys meet certain quality standards for die casting applications. It sets minimum requirements for things like tensile strength at least 310 MPa and elongation no less than 3%, all tested using agreed upon methods across the industry. When it comes to military work though, there's another layer called MIL-STD-2175 that takes things further. This one actually simulates real combat conditions, so parts need to withstand salt spray corrosion tests lasting over 1,000 hours. Plants that follow both standards tend to produce parts with far fewer dimensional issues during high pressure die casting processes. According to recent data from ASM International in 2023, such facilities see about a 42% drop in dimensional deviations compared to those only meeting basic ISO standards.
Strategy: Evaluating Material Test Reports and Process Validation Under Military and Industrial Specifications
Top die casting plants combine mill test reports (MTRs) with things like PPAP when working on defense contracts. Most quality auditors want to see proof that suppliers actually check the metal composition using spectrometers for every batch they produce. They also look for detailed records showing temperature and pressure during production that follow ASTM E2931 standards. And for parts that really matter, like those used in critical systems, X-ray inspections need to cover at least 95% of the casting area. All these checks together make a big difference. Factories implementing this approach report around 37% fewer warranty issues specifically in medical implant applications. For companies bidding on government work or high stakes manufacturing, building relationships based on proper certifications has become standard practice across the industry.
Using Certifications to Evaluate and Mitigate Risk in Global Die Casting Supplier Selection
Certifications provide a standardized framework for assessing die casting factories, reducing time-to-market and due diligence costs in cross-border partnerships. A 2024 supply chain risk study found that companies prioritizing ISO 9001 and IATF 16949-certified suppliers reduced quality incidents by 34% compared to uncertified partnerships.

How Certifications Streamline Supplier Qualification in International Sourcing
Third-party certifications act as pre-vetted quality checkpoints, enabling buyers to verify process controls without on-site audits, compare factories using uniform industry benchmarks, and eliminate 60% of candidate suppliers lacking essential credentials.
Certifications as Predictors of On-Time Delivery, Audit Readiness, and Long-Term Reliability
Factories maintaining IATF 16949 compliance demonstrate 98% audit pass rates versus 72% for non-certified counterparts, according to automotive supply chain data. Certification renewals require continuous process improvements—critical for maintaining defect rates below 0.5% in high-volume production runs.
Emerging Trend: Digital Platforms for Real-Time Verification of Die Casting Factory Certifications
Blockchain-powered credential systems now enable instant verification of expiration dates for quality certifications, material traceability documentation, and NADCA compliance status updates. This digital shift reduces supplier qualification timelines from weeks to hours while preventing documentation fraud—a $2.6 billion annual problem in industrial sourcing (Supply Chain Integrity Report, 2023).
FAQ
What is ISO 9001 and why is it important for die casting factories?
ISO 9001 is a quality management system standard that helps die casting factories improve processes, reduce defects, and maintain consistent quality through standardized workflows.
How does IATF 16949 certification benefit automotive suppliers?
IATF 16949 extends ISO 9001 by focusing on risk management, traceability, and defect prevention, making it crucial for automotive suppliers to meet quality control demands in the EV sector.
What advantages do NADCA-certified die casting factories have?
NADCA-certified factories adhere to industry benchmarks for surface finish, porosity control, and dimensional accuracy, resulting in significantly reduced defect rates and improved product quality.
Why are material certifications like ASTM and MIL-STD important?
These certifications ensure material integrity and mechanical performance under stringent conditions, which is essential for reliability in aerospace, defense, and medical die casting applications.
How do certifications impact global die casting supplier selection?
Certifications provide a standardized framework for evaluating risk and quality, streamlining supplier qualification, and ensuring reliable partnerships in international sourcing.
Table of Contents
-
ISO 9001: The Foundation of Quality Management in Die Casting Factories
- Understanding the role of ISO 9001 in die casting factory operations
- How ISO 9001 ensures process consistency and quality control through standardized workflows
- Case study: Improved defect rates after ISO 9001 implementation in a mid-sized aluminum die casting factory
- Linking ISO 9001 to customer satisfaction and repeat business in precision parts manufacturing
-
IATF 16949: Ensuring Automotive-Grade Compliance for Die Casting Suppliers
- Why IATF 16949 is Essential for Automotive and EV Supply Chain Partnerships
- How IATF 16949 Enhances ISO 9001 With Risk Management, Traceability, and Defect Prevention
- Trend Analysis: Rising Demand for IATF 16949-Certified Die Casting Factories in Electric Vehicle Production
- Strategy: Validating Supplier Compliance Through IATF 16949 Documentation and Process Audits
-
NADCA Certification: Advancing Technical Excellence in Aluminum and Zinc Die Casting
- How NADCA Sets Industry Benchmarks for Surface Finish, Porosity Control, and Dimensional Accuracy
- Verifying Technical Capabilities: What NADCA Certification Reveals About a Die Casting Factory’s Proficiency
- Case Study: Performance Comparison Between NADCA-Certified and Non-Certified Zinc Die Casting Suppliers
- Market Trend: Growing Buyer Preference for NADCA-Certified Partners in High-Integrity Casting Applications
- Material-Specific Accreditations: ASTM, MIL-STD, and Their Role in High-Performance Die Casting
- Using Certifications to Evaluate and Mitigate Risk in Global Die Casting Supplier Selection




