What is Magnesium Die Casting?
How It Compares to Aluminum and Zinc Die Casting
The magnesium die casting process works under high pressure, injecting molten magnesium alloy into specially designed steel molds to create intricate parts with very tight tolerances. What makes this method special? Well, magnesium has some pretty impressive characteristics, most notably its remarkable strength relative to its weight. Compared to aluminum, magnesium is significantly lighter, which gives manufacturers a real edge when they need to cut down on weight. This matters a lot in cars and airplanes where every ounce counts for both performance and how much fuel gets burned. Research shows magnesium components can weigh around 33 percent less than similar aluminum ones. For companies looking to save money on fuel costs or meet stricter emissions standards, this kind of weight savings translates directly into bottom line improvements across transportation manufacturing sectors.

Zinc die casting does make parts with pretty good precision and smooth surfaces, but when things get hot, it just can't keep up with magnesium die casting. Magnesium alloys hold their shape and stay strong even when exposed to extreme heat, something that matters a lot in industries such as aerospace where components face serious temperature challenges. Industry research consistently shows that magnesium parts keep performing reliably under thermal stress conditions while zinc parts tend to degrade faster. That makes magnesium the obvious choice for applications where heat resistance is critical.
By understanding these differences, manufacturers can make informed decisions about materials, aligning their choice with specific industry requirements and performance standards.
Advantages of Magnesium Die Casting
Exceptional Strength-to-Weight Ratio
The strength-to-weight ratio of magnesium die casting stands out compared to other materials, making it great choice when designers need lightweight yet strong parts, especially in cars and trucks. The advantage becomes clear when looking at fuel consumption numbers, something automakers care deeply about these days. Studies show magnesium components weigh around 33% less than similar aluminum ones, though real world results vary depending on design specifics. Lighter vehicles burn less gas obviously, but there's another angle too – meeting those ever tightening emissions regulations has become table stakes for manufacturers. That's why we're seeing more magnesium use across different industries where engineers want to cut down on overall weight while still keeping things sturdy enough to handle everyday wear and tear.

Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Magnesium alloys have decent thermal conductivity around 60 to 100 W/m K which makes them suitable for thermal management in various applications across electronics and automotive sectors. Parts that need to handle temperature regulation benefit from this characteristic, so we often see magnesium used in components throughout both automotive manufacturing and electronic device production. Although magnesium isn't quite as good at conducting electricity as copper or aluminum, it still works well enough for things like EMI shielding housings and creating lightweight cases for electronic devices. This has actually helped push forward some interesting developments in technology over recent years. With growing market needs for lighter yet high performing electronic components, magnesium die casting continues to provide practical answers thanks largely to those inherent conductive qualities.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Magnesium alloys stand up pretty well against corrosion, especially after getting treated right or coated properly for tough environments. Most folks protect them using techniques like MAO coating, conversion coatings, or what's called E-coating through electro deposition. These treatments really boost how they handle rough conditions. Some tests show magnesium actually beats aluminum in certain corrosive situations, as long as those surface treatments stick around and the environment isn't too harsh氯ide heavy or anything. Parts made this way keep working longer term without giving up, even when things get rough out there. For car makers and aerospace companies, this kind of toughness matters a lot since their components need to last and function reliably. When engineers get the surface treatment right, magnesium die cast parts hold together structurally and resist rusting for years on end. The bottom line? Magnesium die casting gives products extra lifespan where durability just has to be top notch.
Incorporating these advantages, magnesium die casting proves to be an exceptionally versatile and efficient process, capable of meeting the rigorous demands of industries focused on sustainability, performance, and technological innovation.
The Die Casting Process for Magnesium Alloys
High-Pressure Die Casting Techniques
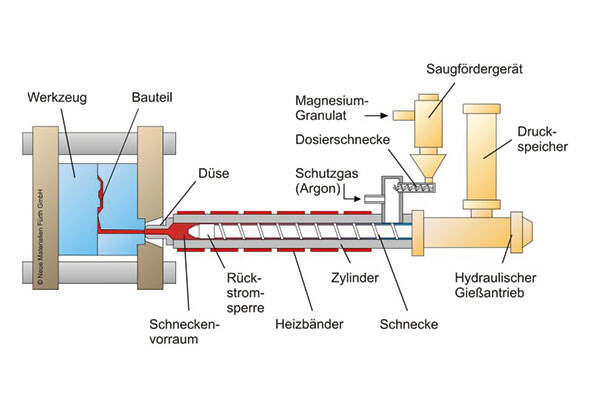
High pressure die casting remains the go to approach when it comes to producing magnesium alloy parts. The process involves injecting molten metal under intense pressure, sometimes reaching over 1000 bar, into specially designed dies. Most setups work with pressures between 500 and 1200 bar, though this varies based on factors like what kind of magnesium alloy is being used, how complicated the part needs to be, and the specifics of the die itself. What makes this technique so valuable is its capability to produce really intricate shapes with exceptional precision. For manufacturers needing smooth finishes and exact measurements, this method delivers outstanding results. Surface roughness can get down to around Ra 1.6 to 3.2 micrometers, while dimensions stay within plus or minus 0.05 mm, which meets pretty strict industry specs. Automotive makers love this process for engine components and structural parts, while aerospace companies rely on it for aircraft interior panels and other complex assemblies. Compared to older manufacturing techniques, magnesium allows for creating these detailed components with much greater accuracy than was previously possible.
Innovations in Vacuum and Semi-Solid Casting
Recent improvements in vacuum die casting and semi-solid casting methods have made a real difference in how we work with magnesium die casting today, cutting down on defects while getting better results from the materials themselves. Vacuum assisted HPDC works wonders for reducing those pesky air bubbles and porous spots that weaken parts, which means stronger components that actually hold up when welded together. When it comes to semi-solid casting, what people call thixomolding lets us shape magnesium granules into finished parts at much lower temps than before. This cuts down on oxidation problems and gives us those nice clean surfaces everyone wants. The SSM family of processes, including both thixomolding and rheocasting, brings some serious advantages too. We get much better control over the microscopic structure of our castings, leading to parts that are mechanically sound and dimensionally stable across batches. For thixomolding specifically, the magic happens around 570 to 620 degrees Celsius where the alloy stays in this sweet spot between solid and liquid states. The semi-solid slurry flows smoothly without all that turbulence seen in regular casting methods, leaving behind far fewer voids in the final product. These new approaches aren't just making things faster to produce either they're saving materials and money at the same time. Manufacturers looking to green their operations find these techniques particularly appealing because they reduce waste while still delivering top quality magnesium components for everything from automotive parts to aerospace applications.
Key Applications in Modern Industries
Electric Vehicle Components (EV Batteries, Frames)
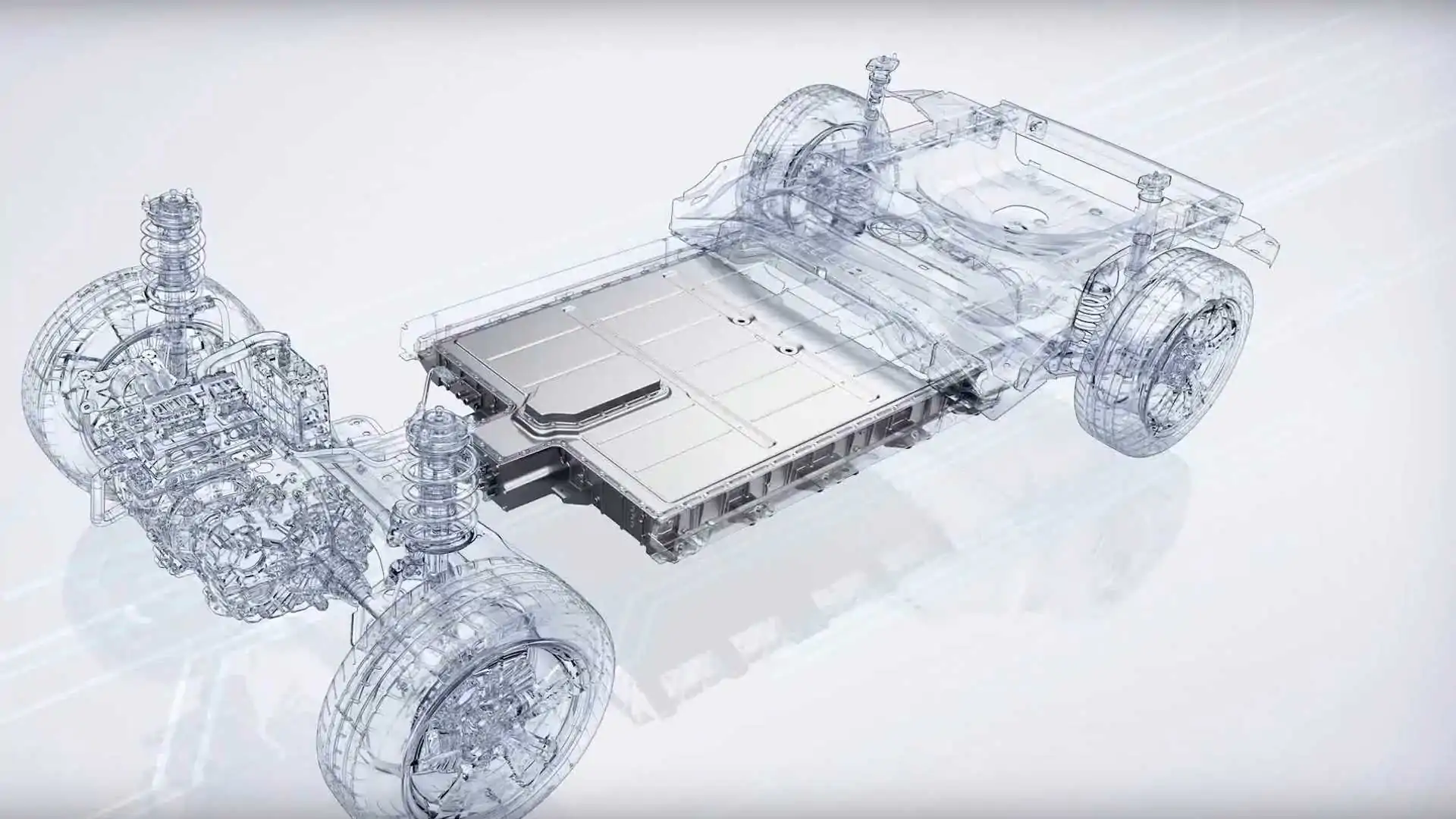
Magnesium die casting plays a major role in making parts for electric cars these days, especially when it comes to creating battery cases and building structural frames. The main benefit? Magnesium alloys cut down on weight quite a bit compared to other materials. Lighter components mean better energy efficiency for the vehicle, longer driving ranges between charges, and generally improved performance on the road. With more people moving away from gas powered cars and toward electric options, manufacturers need more magnesium cast parts than ever before. This growing demand highlights how important die casting technology remains as the automotive industry continues its transition to cleaner transportation solutions.
Aerospace Structural Parts
Aerospace manufacturers rely on magnesium die casting to produce structural parts that hold up under harsh conditions during flights. Magnesium alloys offer an excellent balance between strength and weight, making them perfect choices for building aircraft components that need to be both strong and light enough to improve fuel efficiency and overall safety. Engineers working on planes often point out how magnesium performs better than many alternatives when it comes to handling stress without adding unnecessary bulk. We see this material being used throughout various parts of modern aircraft including interior panels, electronic housing units, and mounting brackets for navigation systems. With airlines constantly looking for ways to cut costs while maintaining quality standards, the demand for these types of lightweight but tough materials keeps growing, ensuring magnesium die casting stays at the forefront of aerospace innovation for years ahead.

Sustainability and Market Growth
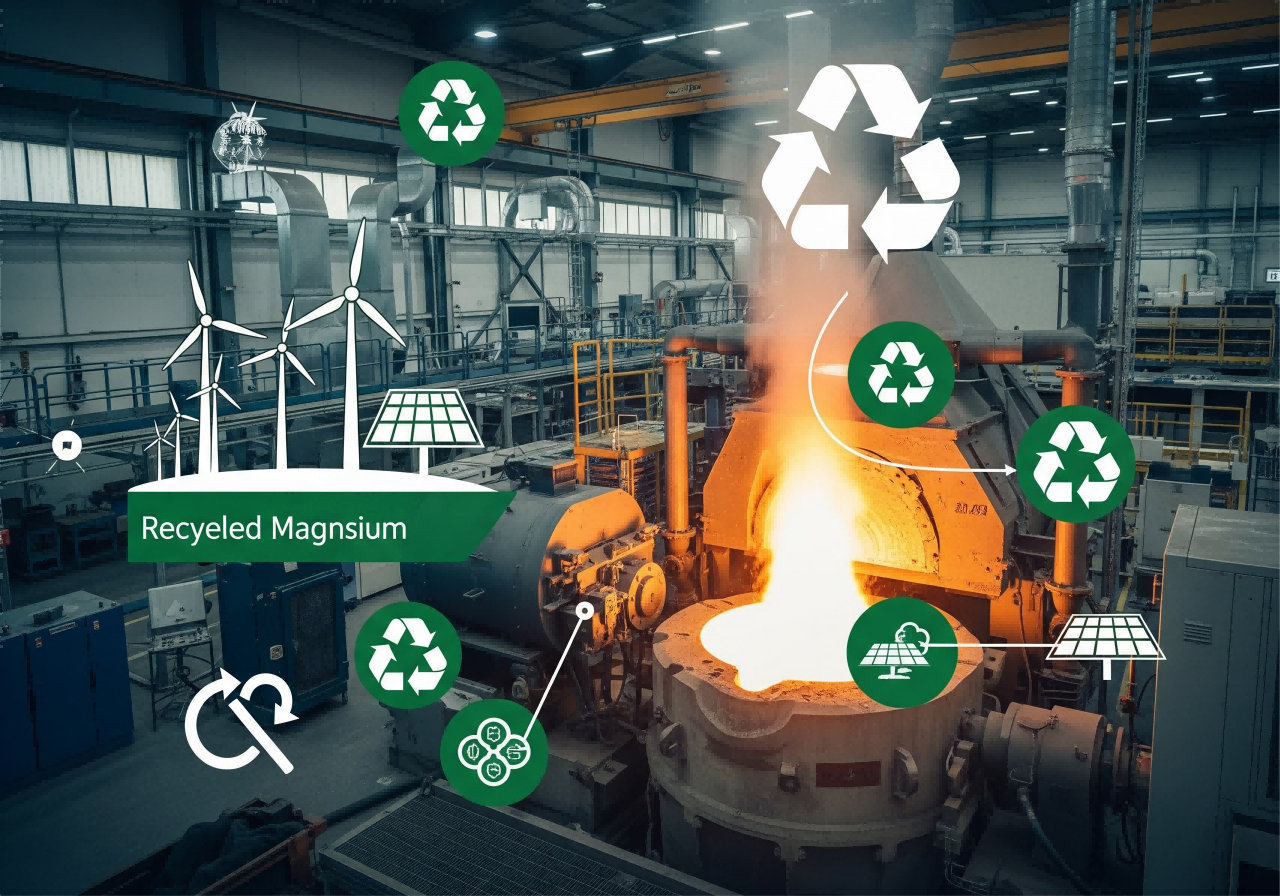
Recyclability and Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
What makes magnesium so appealing for green manufacturing? Well, it can be recycled 100%, which cuts down on carbon emissions during production. When we look at composite materials or those made from multiple components, none compare to magnesium when it comes to keeping their strength after being melted down repeatedly. That quality makes magnesium a great fit for circular economy approaches where materials get reused rather than discarded. With companies across many sectors now prioritizing sustainability, magnesium has become quite popular lately. Market analysts predict demand for recycled magnesium will keep growing, especially since recent research keeps pointing out all the benefits. The metal fits right into the current trend toward greener manufacturing practices because it helps cut back on waste and saves resources overall. Another big plus? Magnesium melts at around 650 degrees Celsius, much lower than aluminum at 660 or steel which needs over 1500 degrees. This means factories use less energy when working with magnesium both during initial casting and subsequent recycling efforts, giving it another edge in the environmental department.

Emerging Trends in Automotive Lightweighting
Car manufacturers are really pushing to make vehicles lighter these days because they want better gas mileage and lower pollution levels. Magnesium die casting has become quite popular in this area. According to various market reports, we should see continued interest in using magnesium for car parts over the coming years. Why? Well, magnesium offers great strength while being much lighter than other materials, which makes it pretty attractive for certain components. Automakers are starting to look at magnesium options for things like dashboards, seat structures, gearboxes, and even battery cases. These are all places where cutting weight actually matters a lot for how efficient the car runs. When companies switch to magnesium die casting processes, they typically save several pounds per vehicle. This not only helps meet those tough emission standards but also means cars perform better on the road, especially when it comes to acceleration and handling characteristics.
With its exceptional balance of performance, weight efficiency, recyclability, and manufacturing versatility, magnesium die casting is poised to play a leading role in the next generation of sustainable industrial design.
Â




