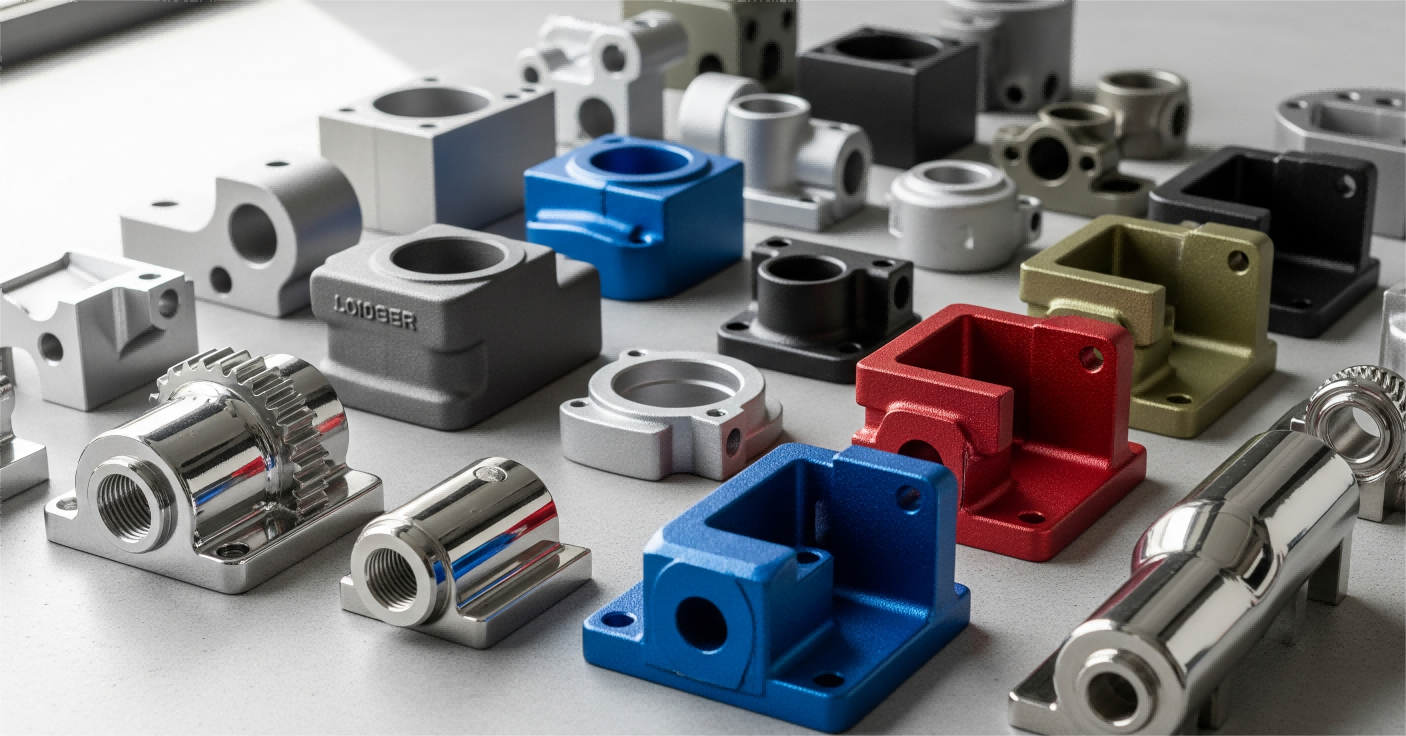
What Is Surface Treatment and Why It Matters in Casting
Surface treatment modifies a material's outermost layer through thermal, chemical, or mechanical methods to enhance functional and aesthetic properties. In investment casting, these techniques improve corrosion resistance, wear durability, and coating adhesion. Without proper treatment, components may fail prematurely due to environmental stressors like oxidation.
Modern casting applications require surface treatments that meet industry standards for safety and performance. Techniques like laser cleaning or chemical etching remove impurities, while abrasive blasting creates uniform textures for better coating adhesion. These processes ensure castings meet stringent requirements in aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where material reliability impacts operational safety.
The Dual Role of Surface Treatment: Aesthetics and Functionality
Surface treatments bridge engineering necessity and design vision. Functionally, methods like electroplating add protective zinc or nickel layers to steel castings, extending service life in corrosive environments. Simultaneously, electropolishing creates reflective surfaces for consumer-facing products like architectural hardware.

The automotive industry exemplifies this dual focus: powder-coated engine components resist high temperatures while maintaining professional appearance. By addressing both practical and visual demands, surface treatment enables manufacturers to deliver high-performance components with brand-consistent finishes.
Key Surface Treatment Methods for Investment Casting Finish
Powder Coating and E-Coating: Protection with Professional Appearance
Powder coating electrostatically applies dry pigments to metal surfaces, forming a resilient layer when heat-cured. E-coating uses an electric current to bond paint molecules, achieving precise thickness control in complex geometries. Both techniques provide durable finishes for automotive components and industrial machinery.
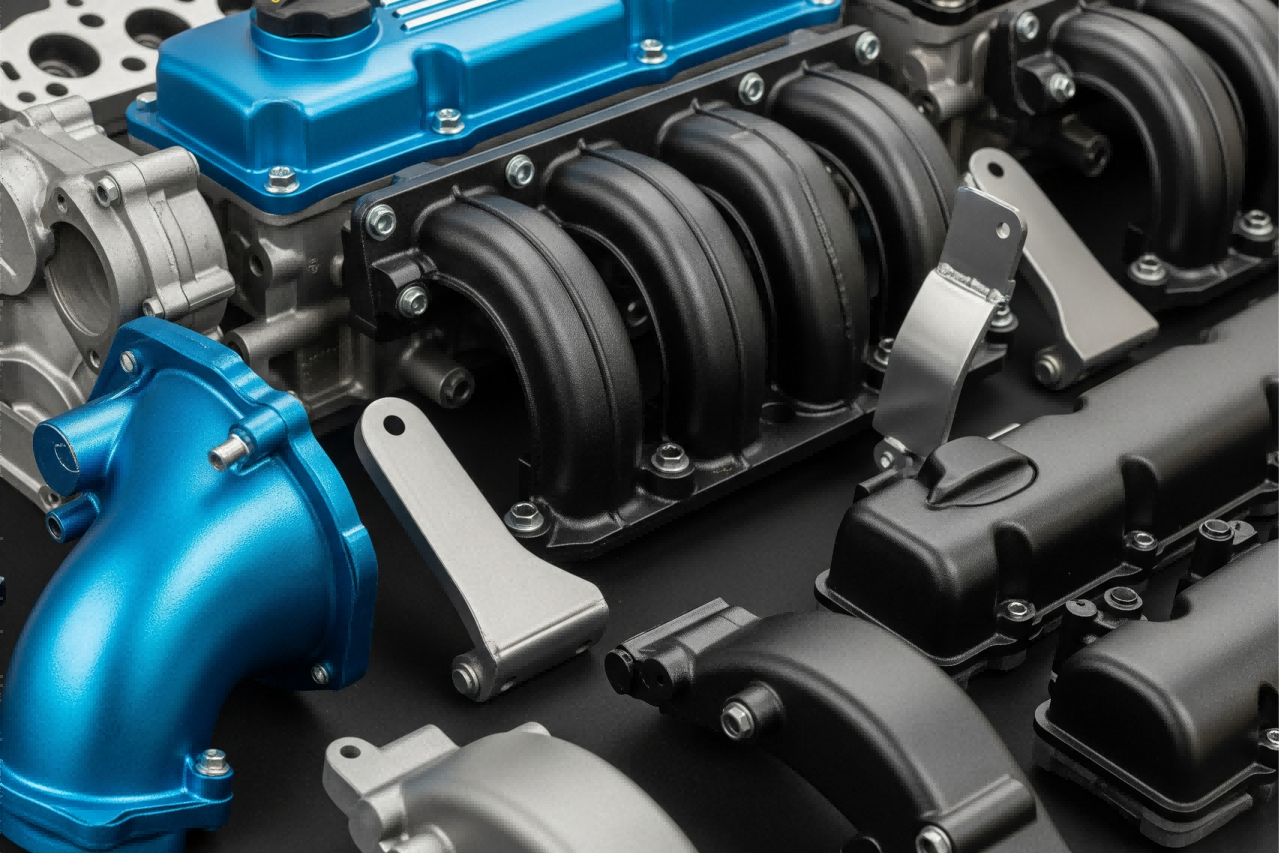
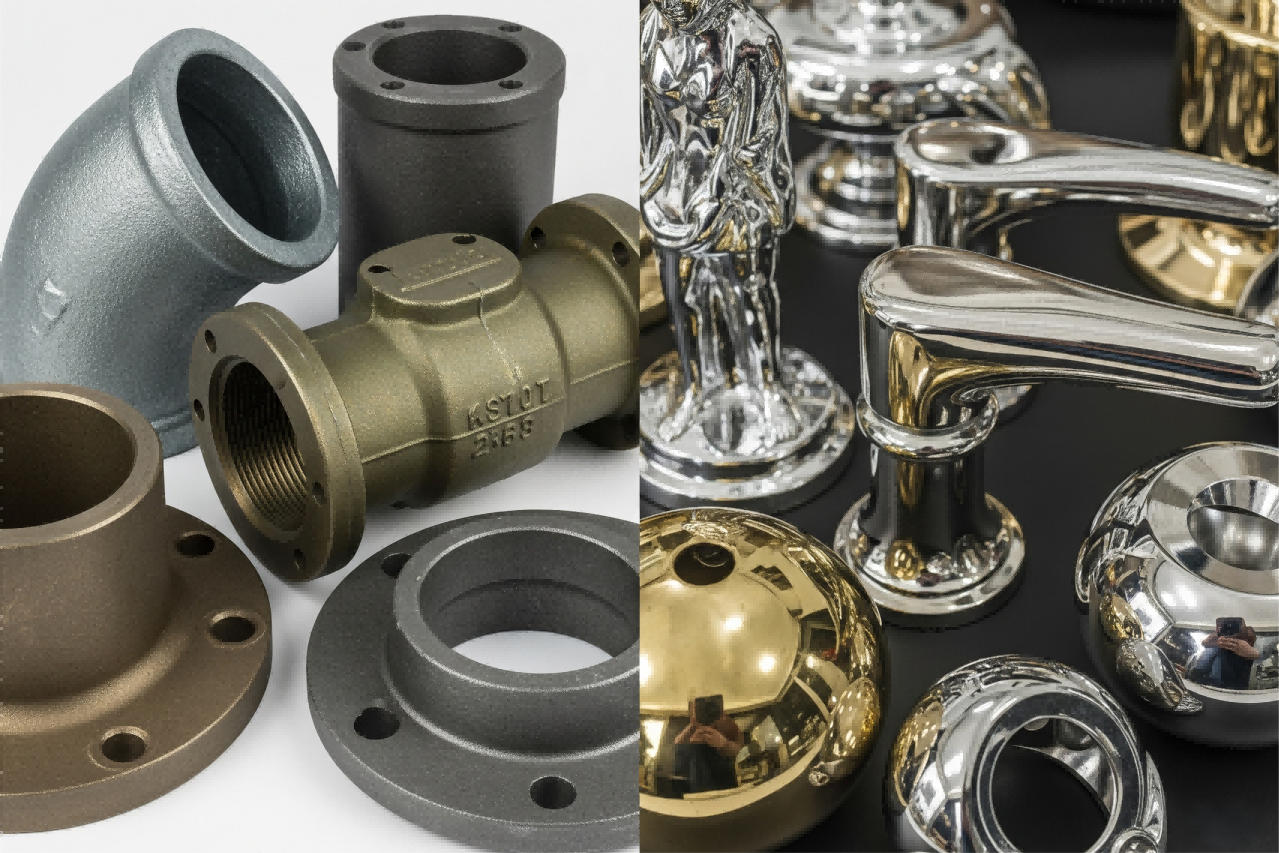
Electroplating and PVD Coating for Durability and Shine
Electroplating deposits metals like chromium or zinc through electrochemical reactions, enhancing surface hardness. PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) creates micrometer-thin coatings in a vacuum, offering exceptional wear resistance. These methods are preferred for luxury hardware and aerospace components.

Sandblasting and Abrasive Finishes for Uniform Texture
Abrasive blasting propels particles to clean surfaces and create consistent matte textures, improving paint adhesion for engine parts and structural components.
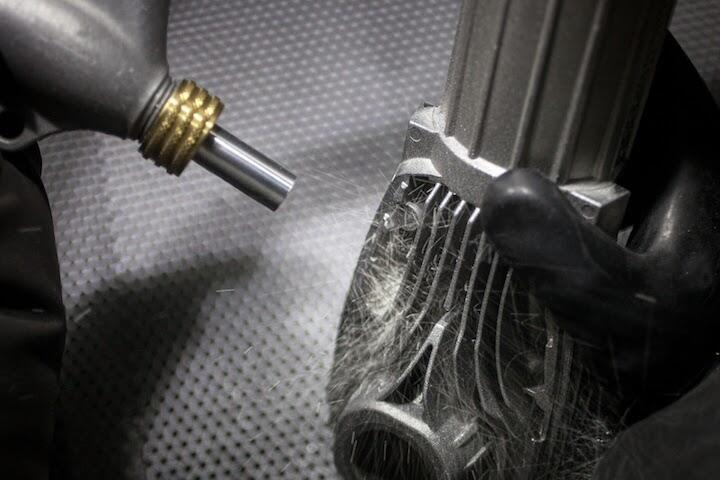

Polishing and Electropolishing: Achieving Mirror-Like Surfaces
Mechanical polishing eliminates imperfections through sequential abrasion, while electropolishing dissolves surface layers chemically. These finishes are critical for medical instruments and food processing equipment where smooth surfaces prevent bacterial growth.
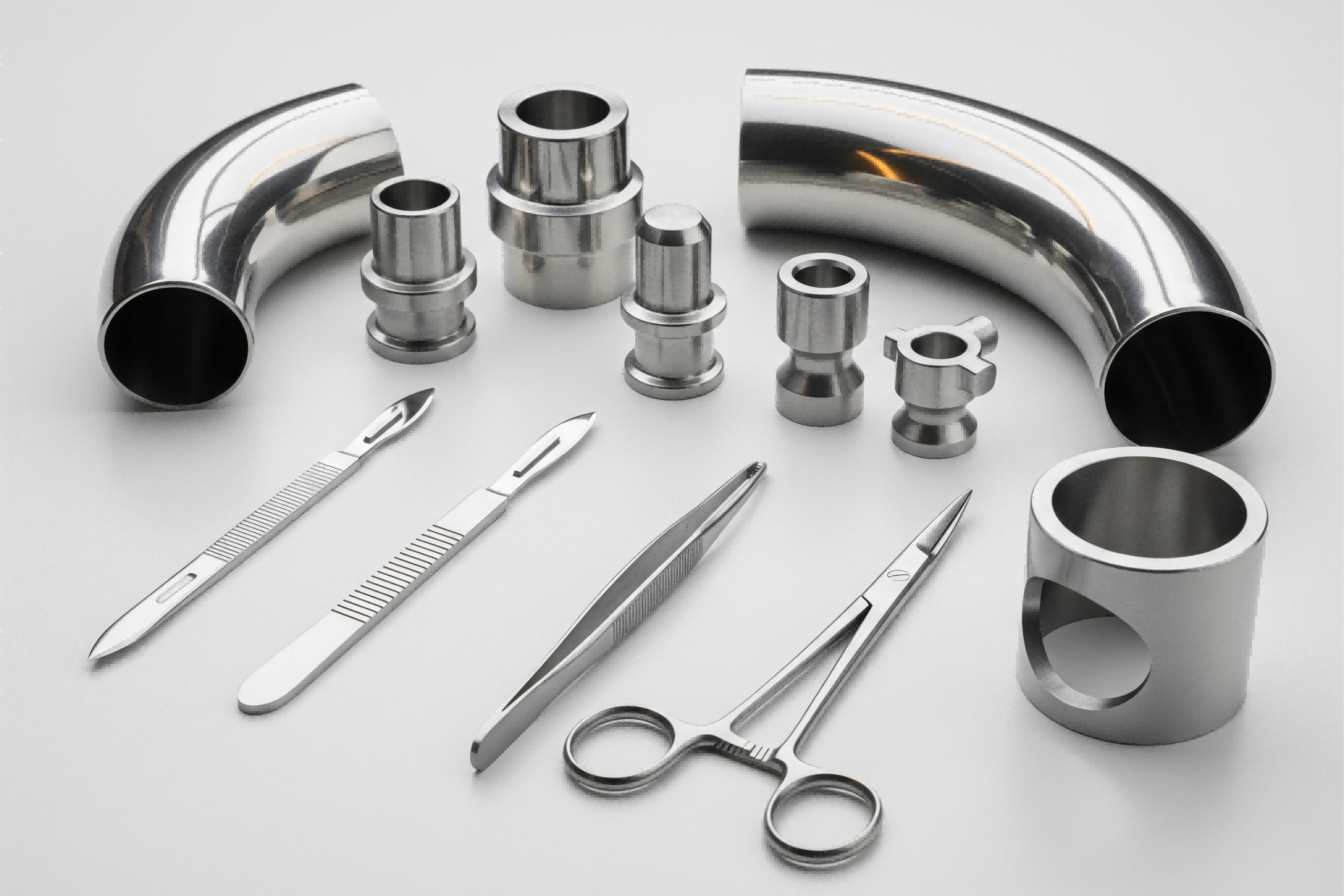

Functional Benefits: Corrosion Resistance and Long-Term Durability
How Surface Treatments Enhance Corrosion Resistance
Surface treatments create barriers against corrosive elements like moisture and chemicals. Chromium-based treatments form passive oxide layers that inhibit corrosion even in high-humidity environments. Industrial equipment with advanced surface treatments requires fewer replacements due to corrosion.
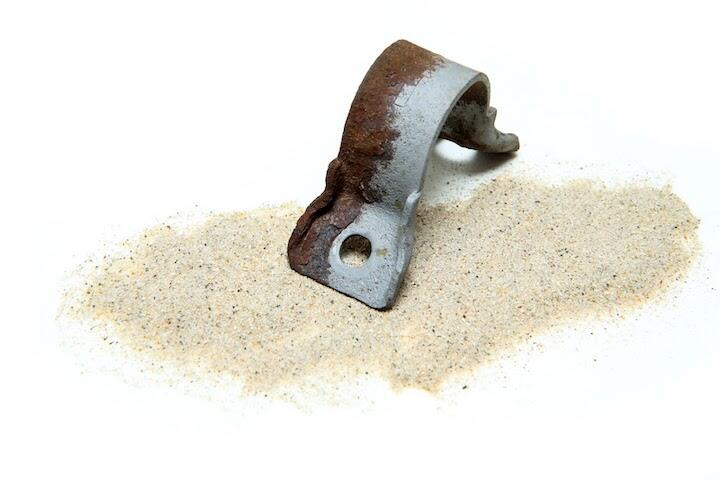

Phosphate Coating, Black Oxide, and Other Protective Layers
| Treatment | Thickness (μm) | Primary Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphate Coating | 2‒12 | Automotive components | Enhances paint adhesion & corrosion resistance |
| Black Oxide | 1‒3 | Tools, fasteners | Provides mild corrosion resistance with matte finish |
| Anodizing | 5‒25+ | Aerospace parts | Forms hard, dielectric oxide layer |
Phosphate coatings create crystalline layers that absorb protective oils, while black oxide offers sleek aesthetics with humidity resistance. For extreme environments, zinc-nickel electroplating surpasses 1,000 hours in salt spray tests (ASTM B117). Layered approaches extend product lifespans by 8‒12 years in infrastructure projects.
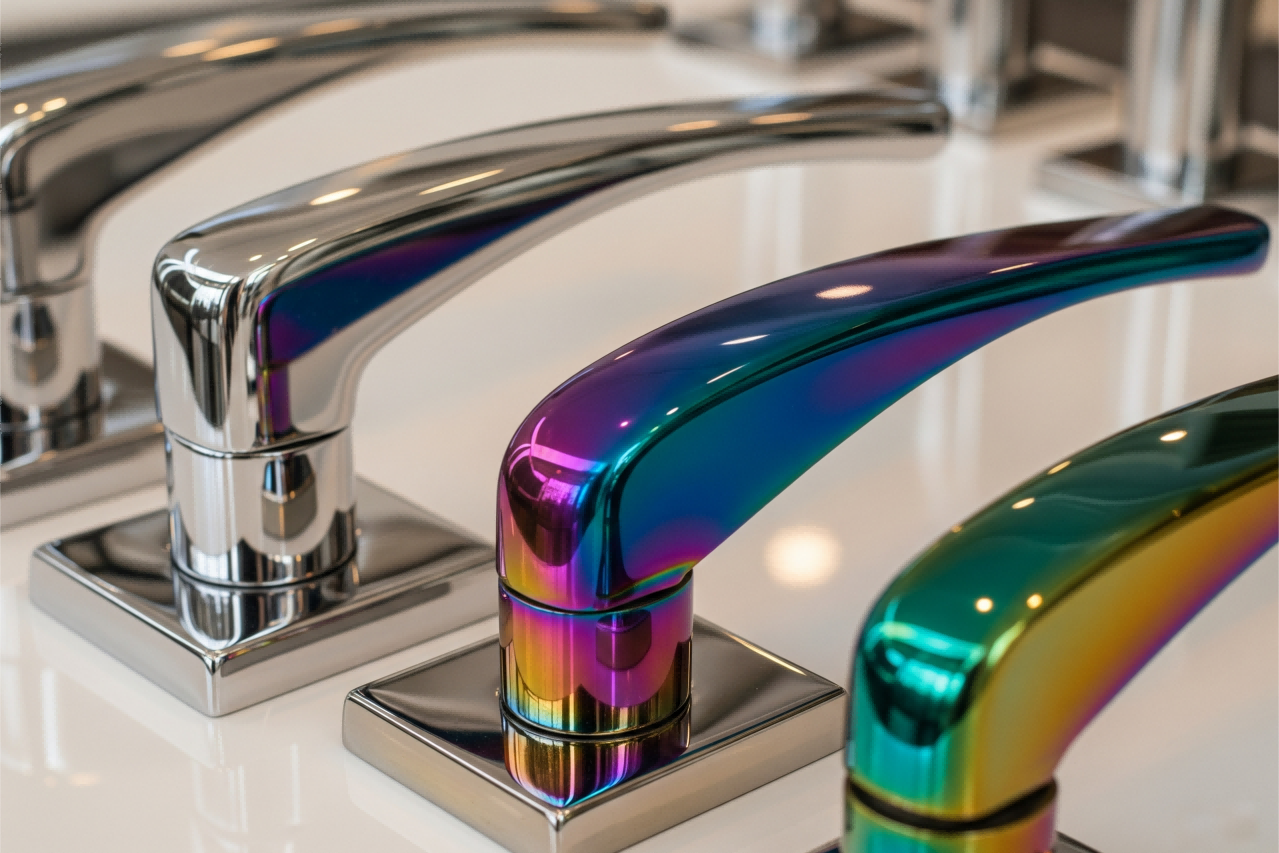
Aesthetic Customization: Aligning Surface Finish with Brand and Design
Laser and Mechanical Texturing for Precision Aesthetics
Laser etching and CNC-guided texturing create intricate patterns that align with brand-specific designs. These methods achieve micron-level precision for logos or custom textures without compromising structural integrity. Diamond-tipped engraving produces wear-resistant markings that maintain visual clarity in harsh environments.
Balancing Industrial Performance with Visual Appeal
Modern surface treatments merge protection with aesthetics through advanced coating techniques. Matte black e-coating reduces glare while projecting a sleek image. Components with coordinated finishes see faster adoption in consumer-facing industries. Ceramic-embedded powder coatings ensure brand colors remain vibrant throughout a product's lifecycle.
Innovations and Selection: Advancing Surface Treatment in B2B Casting
Emerging Trends: Automation in Polishing and Advanced Coating Efficiency
Robotic polishing systems with machine vision achieve micron-level precision across complex casting geometries. These AI-driven surface treatment systems enable real-time adjustments, reducing material waste. Advanced coatings like nanoparticle-enhanced PVD offer environmental and performance benefits for aerospace and medical components.
How to Choose the Right Surface Treatment for Your Casting Needs
Selection criteria include:
- Material Compatibility: Aluminum requires different coatings than stainless steel
- Environmental Exposure: Marine components need superior corrosion resistance
- Mechanical Stress: High-wear parts benefit from hardened coatings
- Production Scale: Automated processes become cost-effective for large volumes
Prototype testing reduces treatment-related defects during production scaling. For critical applications, combine electropolishing with protective PVD coatings to achieve both smoothness and chemical resistance.
FAQ Section
What is the primary purpose of surface treatment in casting?
Surface treatment in casting primarily aims to enhance both the functional properties (such as corrosion resistance and durability) and aesthetic appeal of cast components.
What are common methods used for surface treatment in investment casting?
Common methods include powder coating, electroplating, PVD coating, sandblasting, polishing, and electropolishing, each offering unique benefits for various applications.
How does surface treatment enhance corrosion resistance?
Surface treatments create protective barriers against corrosive elements, such as chromium-based treatments that form passive oxide layers to inhibit corrosion.
How can manufacturers select the right surface treatment for their needs?
Manufacturers should consider material compatibility, environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and production scale to select the most appropriate surface treatment process.
Why is surface treatment important for aesthetics in casting applications?
Surface treatment enhances aesthetic appeal by allowing customization of textures and finishes to align with brand and design specifications, facilitating faster consumer adoption.
Table of Contents
- What Is Surface Treatment and Why It Matters in Casting
- The Dual Role of Surface Treatment: Aesthetics and Functionality
- Key Surface Treatment Methods for Investment Casting Finish
- Functional Benefits: Corrosion Resistance and Long-Term Durability
- Aesthetic Customization: Aligning Surface Finish with Brand and Design
- Laser and Mechanical Texturing for Precision Aesthetics
- Balancing Industrial Performance with Visual Appeal
- Innovations and Selection: Advancing Surface Treatment in B2B Casting
- FAQ Section




